Introduction
From the Swiss School of Management in collaboration with LawSikho!
The official announcement of the Swiss School of Management about this program and the collaboration with LawSikho on their website is here.
In the information age, no business can function without data. Data drives every critical decision, and even entire business models are created around data. From evaluating marketing strategies, predicting sales, performance management, and identifying potential revenue sources to designing new products, data enables smarter decisions.
The importance of data has led to the slogan “data is the new oil” to highlight the unlimited opportunities and possibilities hidden in the world of data and its central role in modern business.
However, the risks of misuse of this data are incredibly high.
From phishing scams, ransomware, cyber blackmailing, impersonation, and cyber terrorism to spam, breaches in data privacy lead to many expensive and damaging disasters for businesses, governments & regulators and alarming for individuals.
In April 2020, more than 500,000 Zoom accounts were breached and sold on the dark web and hacker forums. This data was used to impersonate a person, eavesdrop on meetings and send malware files or documents to create a data breach chain. An incident of cyber terrorism created a power outage in Mumbai for hours. Indian fintech startup Mobikwik was looking at an IPO in 2022, but that looks uncertain now, thanks to a data breach that affected millions of users.
These are just a few examples but may help to highlight the seriousness and scale of the problem.
The average cost of a data breach for a company in 2020 was $3.86 million.
As per TechJury, 30,000 websites were hacked globally every day in 2020.
Over 22 billion records were exposed worldwide amid 730 publicly disclosed data breaches in 2020 alone.
These breaches affected organisations such as Microsoft and social media giants such as Twitter, Dubsmash and Zynga.
Not only large tech companies but startups are equally affected.
As per a Verizon Business 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, 28% of data breaches in 2020 involved small businesses.
Some examples of startups that have faced data breaches since 2020 are:
- Digital Ocean, a cloud infrastructure company, met a data breach in 2021, which affected 1% of the customers’ billing data
- US-based risk startup LogicGate suffered a data breach but did not disclose details in public - it only intimated customers directly and regulatory authorities under applicable laws
- Australian security house Click Studios suffered a data breach involving the leak of passwords through its password manager PasswordState
- Mercato, a grocery delivery startup in the US, whose customer data from 2015-2019 was breached in 2021
- Ubiquiti, a networking gear seller, faced a severe data breach targeting its cloud-based data on its Amazon Web Services accounts
- Shopify suffered a data breach targeting less than 200 merchants’ data in September 2020
- Juspay, a payment processing company, data breach leading to the leak of over 100 million digital payments transactions
- Unacademy, one of the most talked-about revolutionary startups in the tech industry, faced a breach causing a data leak of more than 20 million records.
- Whitehat Jr - ed-tech startup suffered a data breach of over 250,000 records
- Dunzo - 3.4 million users’ data exposed
- BigBasket - 20 million users’ data
- Cybercrime is expected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
To minimise the risk and damage from misuse of this data, governments across the world have created laws, regulations, and frameworks to protect the data of consumers, employees, organisations, and users and ensure the privacy of individuals globally. Most countries have given privacy the status of a human right.
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), 128 out of 194 countries have enacted legislation to secure data and privacy protection.
This trend has led to the emergence of specialised careers for lawyers who cater to the data protection and privacy management needs of Big Tech companies and startups and SMEs - both as in-house counsels and external lawyers.
For example, when the EU GDPR was rolled out, Facebook started preparing by deploying a product director and an in-house privacy lawyer, designated as the ‘Chief Privacy Officer’ to prepare for the rollout.
It’s not just tech companies anymore, but all other businesses also need to comply with data protection laws, leading to the rise of a new area of practice for lawyers and a new professional discipline of management.
Data protection and privacy management is now a critical aspect of running any business. Failure can lead to compromised reputation, huge fines, regulatory curbs, public backlash and loss of business.
Global law firms and large consultancy firms are building up dedicated privacy and data protection teams to cater to this need - Legal 500 recognises “Data Protection and Privacy” as a separate practice area for ranking law firms across jurisdictions.
The pandemic increased the need for privacy protection as the volume of interaction and transactions concluded online multiplied exponentially across the world.
This trend points to a fast-growing need for lawyers in the data protection and privacy space.
The applicability of EU GDPR to offshore organisations alone led to a requirement of 75,000 DPOs.
This does not consider the openings for non-GDPR DPOs, to help organisations comply with data protection laws in other countries.
Even if you do a quick search, you will find many international and domestic openings in the area of data protection and privacy.
The number of jobs in developing countries like India also remains high.
Last-mile customer data is vital for an organisation to identify trends to optimise its production, marketing and sales strategies, which is why data protection is becoming inevitable even for non-tech companies.
If an organisation deals with data, the implementation of a privacy program is not optional.
Penalties for non-compliance are very high - in the European Union, for example, aggregate fines levied for violation of data protection norms is €261,192,138 as of January 2021 imposed in the last three years.
Global clients will refuse to work with an organisation if it lacks essential data protection and privacy compliance systems because the data of their employees or customers are at risk, exposing them to a considerable risk of fines and reputational damage.
On the other hand, qualified professionals with experience in data protection and privacy management are few and far between. Businesses struggle to find experts in this area.
This is why job opportunities in data protection and privacy management are exploding.
Who leads the data protection and privacy initiative in an organisation?
Internal and external teams are comprising privacy and data protection lawyers, who can guide other business teams such as product, tech, sales and marketing to implement these insights.
The team is usually headed by a Chief Privacy Officer, a lawyer with specialised domain knowledge and a deep practical understanding of privacy and data protection laws.
What kinds of jobs can I secure in the field of data protection and privacy?
The most common job designations for data protection and privacy-related roles are as follows:
- Data Protection Officer - lawyers, are exceptionally suited for this role
- Privacy Counsel
- Privacy Officer or Chief Privacy Officer
- Legal specialist- Contracts and Privacy
- Privacy specialist
- Associate - data protection and privacy management
How much can you earn in these roles?
As per J.W. Michaels, compensation for in-house privacy law team members across a range of Silicon Valley and Washington State Companies indicated compensation at approximately USD 220,000 with up to 25% additional compensation coming in the form of equity.
Let us examine what a Data Protection Officer earns across jurisdictions.
- Europe: As per GDPR.CASH, a network of GDPR experts, the average annual salary of a data protection officer (DPO) in Europe is as high as €71,584.
- US: As per GDPR.CASH again, the annual salary of an Officer equivalent to a DPO is approximately $150,000.
- UK: As mentioned in UK’s talent.com, entry-level DPOs earn £28,000, while experienced DPOs are £74,489 per year.
- India: As per Glassdoor, the average annual salary of a Privacy Officer or a Privacy Consultant in India begins from ₹15 lacs and goes up to ₹1 crore for senior roles.
Note that it is not just a Privacy Officer who can handle an entire organisation's data and privacy management. Depending on the volume of data and complexity of processes involved, junior members must be hired in privacy and data protection roles. There are a lot of entry-level jobs that are also getting created for this reason.
Trends that are fuelling further growth of data protection and privacy management as a profession
#1 - Remote work and virtual offices have increased cybersecurity threats
A website called Government Technology explains that 2020 brought in not just the COVID pandemic but a cyber pandemic, with several global companies facing cyber attacks, which were captured in international headlines.
The World Health Organization’s website alone faced five times more attacks in 2020!
Vulnerability to attack in a remote work environment has increased because employees log in through the general internet through multiple networks and devices.
#2 - Talent arbitrage is opening new doors for lawyers interested in performing data protection and privacy work
There is an increasing need to adhere to data protection systems of multiple jurisdictions for any global startups, tech companies and MNCs unless you do business in just one country. There is also research, drafting and compliance work that can be delegated to international remote workers. This has created a unique opportunity for privacy professionals in developing countries to do remote freelance work or full-time work for advanced economies.
It is not necessary that an internal or external DPO or their staff must work on-premises, or be legally qualified to practice in the jurisdiction where the organisation operates. Of course, there can be issues related to the international cross-border transfer of data. Still, as long as one is not processing or acting as a custodian of such data, foreign remote professionals can work in privacy and data management teams.
This opens up opportunities for young lawyers from economies in India, Africa, South Asia, etc., trained in global privacy and data protection laws, management principles and best practices and are familiar with multi-jurisdiction regulations.
#3 - International expansion and globalisation has led to the increased global regulation of data privacy
Universal internet penetration, affordable mobile devices, cheap broadband connectivity and then the pandemic have accelerated globalisation. Still, governments have been concerned about the free flow of data globally across the internet and the possible risks, which has led them to enact data protection legislation.
Since 2018, starting with the EU GDPR, several world economies have enacted data protection legislation.
- Brazil passed a data protection legislation in September 2020
- Canada is considering a new Digital Charter Implementation Act to replace its privacy law
- UK has enacted its data protection law, largely modelled around EU GDPR, which is applicable post Brexit
- In the US, a new privacy law was introduced in November 2020
- Australia plans to complete a review of its privacy legislation in 2021
- China is considering a draft data protection legislation
- Several African countries have passed data protection and privacy legislations since around 2010, even predating the EU GDPR
#4 - Privacy awareness amongst users
Increased user awareness through various incidents such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal, Wikileaks, outcry against change in policies by Whatsapp and activity by groups such as American Civil Liberties Union on privacy has put pressure on companies to safeguard user privacy more diligently and on governments to enact and implement privacy legislation strictly.
Why developing countries like India are going to witness an explosion of privacy jobs
India’s Personal Data Protection Bill imposes data localisation requirements for sensitive personal data to be mandatorily stored in India and for any ‘critical personal data to be processed within India only.
Further, foreign companies are required to depute a DPO under the law locally.
Law firms are already conducting a lot of internal research on this, and companies are preparing in advance for the law.
When this law is passed, it will lead to an explosion of privacy jobs.
Since data protection frameworks are constantly evolving, such requirements can be present in the laws of other countries as well.
- Do you want to add a qualification that makes you especially suited for work in Big Tech such as Facebook, Alphabet, Microsoft, Apple and Amazon and at fast-growing international startups?
- Do you aspire to work for organisations focussing on the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence and other cutting-edge technologies of the future? Do you want to know which skills will set you apart?
- Do you want to shift to a business role from your current role as a corporate transactions lawyer or an in-house counsel? Are you wondering what is the next step to take to pursue this future?
- Do you want to identify a niche in technology law that sets you apart from other tech lawyers?
- Do you want to help startups in Silicon Valley solve critical tech-related challenges to grow internationally?
That is where a Masters in Business Administration (MBA) degree with a specialisation in Data Protection and Privacy Management from the Swiss School of Management comes in.
scholarship banner
About Swiss School of Management

Image: University of Washington, Rome Campus, where Swiss School of Management is housed
The Swiss School of Management (SSM) is an accredited private institute of higher education founded in the last century in Switzerland. The school is operating from its campus in the city of Rome, Italy enabling the students to benefit from the EU policy of traveling and working without Visa in 27 member-countries among the European Union.
Short video about campus life and interactions is available here.
SSM is an accredited institution by the Ministry of Education & Research of Italy in its headquarters in the Region of Lazio. It has the following accreditations:
- SSM is accredited by the International Accreditation Council for Business Education (IACBE) for its business and management programs, valid internationally, and CHEA-Council for Higher Education Accreditation, in the US. .
- SSM has been certified by EduQua, a Swiss quality label for further education institutions.
- SSM is a UNESCO approved Institution, through the International Association of Universities.
- The US Department of Veterans Affairs has given full accreditation to the Undergraduate, Postgraduate, and Doctoral programs of SSM.
- The Swiss School of Management is a member of BUSINET.
It is Ranked Top 5 Amongst Global Management Schools - see here.
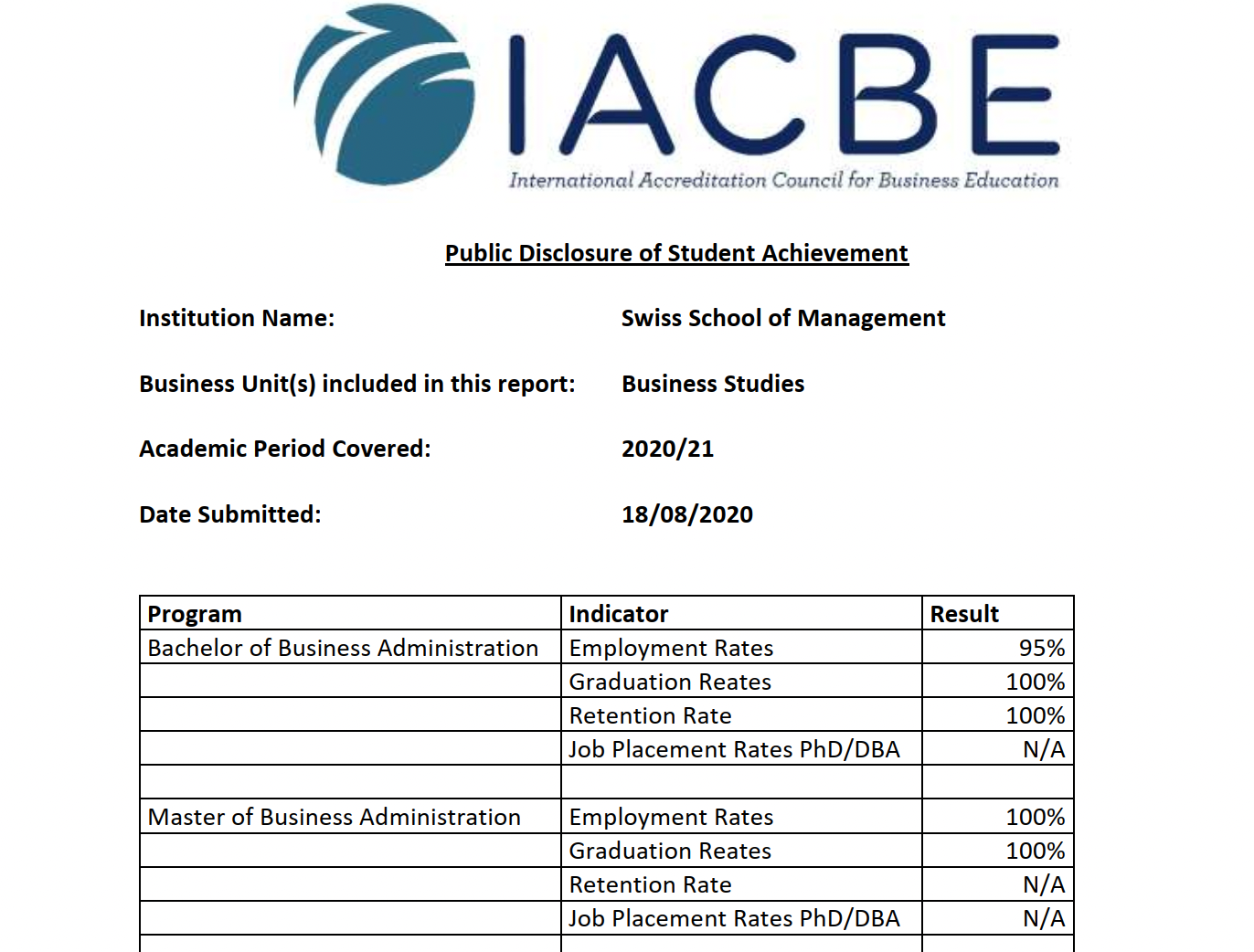
It has 100% completion and 100% placement rate for MBA candidates as per its public disclosure to IACBE.
The School is offering a one-month immersion program too, which includes:
- A visit to the Rome campus of the University of Washington.
- Industry interaction from SSM’s training centre at Aachen (Germany). The students will get to visit a company such as Canon/ Ford Motors/ Bayer/ Extron.
- A visit to the Netherlands (optional).
- You will receive live GDPR problems in each country and make presentations (like the show "Dragons' Den") at the end of the week and have live coaching available at the venue. Target 14 personal meetings with lawyers, data protection professionals in Rome for networking. Our people will be there to guide the students.
The immersion program costs 1,700 Euros or INR 1.5 lakh (this is only tuition and covers no other costs - such as flight, transport, visa & accommodation charges).
Candidates who complete the MBA successfully will be accorded alumni status and be a part of a LinkedIn network for alumni that is being developed.
List of successful alumni profiles and information is here https://ssm.swiss/student-referrals/
MBA degree provides various benefits for international immigration, e.g. Canada (MBA gets 23 out of 67 points), Germany (20 out of 70 points), New Zealand (50 out of 160 points)
Summer School in Rome
The students will be offered an optional intensive summer school at the Rome Campus of the University. Additional fees will be chargeable for such students who opt to participate in that offering.
How is this course different from other online MBA programs?
|
Feature |
Other Technical Certifications and MBA Degrees |
This Course |
|
What type of work do you learn?
|
Learn entry-level work with MCQ-based tests on the law and scenarios, limited study materials and pre-recorded videos.
|
Learn advanced skills to perform real life work - implement privacy by design, drafting multi-jurisdictional privacy policies and data processing agreements, conducting data protection impact assessments, audits, etc. through weekly exercises.
|
|
Training Methodology and Study Materials |
Limited study materials - pre-recorded videos, MCQ assignments, no evaluation, no guidance - difficult to complete and stay motivated in the journey. |
Extensive study materials, 3 hours of live online classroom every week (with recordings), in-line evaluation and feedback on your drafts, training on writing articles and networking, plus periodic calls to keep you motivated. |
|
Placement Assistance and Opportunities to Secure International Freelance Work |
Absent in other certifications and in online MBA programs |
Placement support with assistance on CV Building, improving your online presence, guidance on networking, mock interviews, guidance on securing international freelance projects through platforms such as Upwork, Fiverr, People Per Hour, etc. |
|
Value of Qualification |
It is confusing for recruiters and difficult to stand out merely through your qualification.
The word “Online” in MBA is perceived to be a diluted version in the market, and also the value provided by most universities is a tiny fraction of the offline program. |
Stand out in the crowd with your coursework and MBA degree: there is no other similar MBA program in data protection and privacy management.
Obtain an MBA degree from a Swiss University while studying online. Accredited by the IACBE (European Union Accreditation) and Eduqua (Swiss Government recognition), also recognised in the US |
|
Cost |
Even premier institutes from India charge USD 15,000-38,000 (IIMs), USD 58,000 (ISB), but do not help lawyers and professionals in securing more promising opportunities/ new careers and lawyers are compelled to go back to mainstream lawyering. |
This is a highly specialised program for lawyers, CAs, CS, IT and management professionals who want to transition into this role, available at an affordable price of approximately Euros 15,300/ USD 18,700. |
|
Flexibility and convenience for working professionals |
Working professionals have to either leave their profession to study at a full-time MBA program, or forego the MBA degree and pursue an “executive education” program which provides a certificate or diploma |
You can complete this program without leaving work within 15 months (5 hours per day) to 2.5 years (2.5 hours per day) - use your skills to increase your earnings while you pursue the program |
Who should take this course?
The MBA with Specialisation in Data Protection and Privacy Management at the Swiss School of Management is designed for individuals who aspire to excel in the dynamic field of data protection and privacy management.
This program will help you stay ahead of the curve, making informed decisions, and aligning your organization's strategies with global privacy regulations.
- In today's data-driven business environment, executives and managers must understand the intricacies of data privacy.
- Aspiring privacy officers, compliance managers, and data protection consultants will benefit greatly from our specialized curriculum.
- Lawyers, IT experts, and cybersecurity professionals seeking to expand their skill set and enhance their career opportunities will find this course invaluable.
- Data privacy is crucial for every business, regardless of size. If you're an entrepreneur or founder, this program will equip you with the knowledge to integrate robust privacy measures into your business from the outset, ensuring compliance and building trust with customers.
Are you considering a career change?
Whether you come from a different industry or background, our MBA with Specialisation in Data Protection and Privacy Management welcomes individuals with diverse experiences who are eager to step into the world of data privacy.
What will you learn from this course?
Here are key areas you will learn from this course:
- Gain a comprehensive understanding of core business concepts, including strategic management, marketing, finance, and organizational behavior, providing you with a solid foundation for your specialization.
- Explore global data protection laws and regulations, with a focus on the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and emerging data privacy legislation worldwide.
- Learn how to ensure organizational compliance with data protection laws, including the development and implementation of data privacy policies, procedures, and controls.
- Understand the principles of data security, encryption, and access control to safeguard sensitive information against breaches and cyber threats.
- Master the art of conducting Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) to assess and mitigate privacy risks associated with data processing activities within an organization.
- Explore the concept of privacy by design and learn how to integrate data protection considerations into product and system development processes from the outset.
- Study data governance frameworks and ethical considerations surrounding data collection, processing, and usage in business operations.
- Develop the skills to formulate and execute an effective incident response plan in the event of a data breach, minimizing damage and complying with regulatory requirements.
- Examine the intricacies of cross-border data transfers and the legal mechanisms (e.g., Standard Contractual Clauses) used to facilitate such transfers in compliance with data protection laws.
- Cultivate leadership skills specific to data protection and privacy management, enabling you to guide organizations in navigating the complex landscape of data privacy in an ever-evolving digital world.
By the end of this MBA program, you will be well-prepared to take on key roles in data protection and privacy management, making informed decisions, ensuring regulatory compliance, and safeguarding sensitive data within organizations across various industries.
This specialized knowledge will not only enhance your career prospects but also contribute to the growing importance of data privacy in the global business landscape.
Training Methodology

Online 24/7 access
Access study materials via our online portal & via our anroid & iOS apps.

Practical Exercises
Two practical exercises every week, each followed by written feedback.

Live Online Classes
Live online classes based on exercises, allowing questions and feedback.

Convenient Class timings
Classes held after work hours, typically on Sundays or after 8 PM on weekdays.

Live Doubt Clearing
Live doubt clearing for support and one-on-one sessions with mentors.
What is the career potential after doing this course?
An MBA with Specialization in Data Protection and Privacy Management from the Swiss School of Management opens up a world of exciting career opportunities in the rapidly evolving field of data protection and privacy.
This unique program equips graduates with the knowledge, skills, and expertise needed to excel in a variety of roles within this critical and high-demand sector. Here's a glimpse of the career potential after completing this course:
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): One of the most prominent roles in data privacy, DPOs are responsible for ensuring an organization's compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and more. Graduates with this specialization are well-prepared to take on this pivotal role, overseeing data protection strategies and implementation.
- Privacy Consultant: Companies across industries are in constant need of expert advice on how to navigate the complex landscape of data privacy. Graduates can work as consultants, helping organizations design and implement robust data protection strategies tailored to their specific needs.
- Privacy Compliance Manager: These professionals play a crucial role in ensuring that an organization complies with data protection laws and regulations. They oversee the development of compliance programs, conduct audits, and collaborate with stakeholders to maintain data privacy.
- Cybersecurity Analyst: A solid understanding of data protection and privacy management is essential in the realm of cybersecurity. Graduates can work in roles that involve safeguarding digital assets and protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.
- Legal Counsel for Data Privacy: With their expertise in data protection laws and regulations, graduates can pursue careers as legal counsel specializing in data privacy. They can advise organizations on legal matters related to data protection and represent them in privacy-related legal proceedings.
- Chief Privacy Officer (CPO): As organizations prioritize data privacy, the role of a CPO becomes increasingly vital. Graduates with this specialization can aim for executive-level positions, where they lead an organization's data protection efforts, develop privacy policies, and manage compliance initiatives.
- Information Security Manager: Data protection is closely linked to information security. Graduates can take on roles as information security managers, responsible for creating and implementing strategies to protect an organization's data assets.
- Risk Analyst/Manager: Understanding the risks associated with data breaches and non-compliance is crucial. Graduates can work in risk management positions, helping organizations assess and mitigate data protection risks effectively.
- Entrepreneurship: Armed with a specialized MBA, some graduates may choose to start their own consultancy firms, offering data protection and privacy management services to businesses in need.
The MBA with Specialization in Data Protection and Privacy Management from the Swiss School of Management provides a versatile skill set that is in high demand across various industries and sectors.
As data privacy continues to be a global concern, the career potential for graduates of this program is substantial, offering a promising and rewarding future in the field of data protection and privacy management.
Which industries can you work in if you possess an international MBA degree with a specialisation in data protection and privacy?
- Healthcare: Hospitals, clinics, telemedicine, healthcare startups
- BFSI and Fintech: Banking, financial services, insurance, fintech, investment companies
- Energy: Oil and gas companies, utilities, alternative energy & renewables
- Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical (APIs, generics contract manufacturers, etc.) biotechnology, biomedical & life sciences
- Industrial: Chemical process, engineering manufacturing companies
- Technology: Software (e-commerce, SAAS, etc.) and hardware companies
- Education: Public and private universities and colleges, training and development companies
- Services: Professional services such as legal, accounting and consulting firms
- Entertainment: Movie production, sports, gaming and casinos, OTT
- Transportation: Airlines, railroad, trucking and delivery companies
- Communication: Newspapers, book publishers, public relations and advertising agencies
- Consumer: Manufacturers and distributors of consumer products
- Media: Television, satellite, social media, Internet
- Hospitality: Hotels, restaurant chains, cruise lines
- Retail: Brick and mortar and e-commerce
- Research: Market research, think tanks, R&D
- Public: Federal, state and local government agencies and NGOs
Business teams that you can work in
As an MBA graduate with a specialization in Data Protection and Privacy Management from the Swiss School of Management, you'll find a wide range of exciting career opportunities in various business sectors.
Here are some potential employers and career paths where your expertise in data protection and privacy can make a significant impact:
- Joining the data protection and privacy department of organizations is a natural fit for your specialization. You can contribute to ensuring compliance with data protection laws and safeguarding sensitive information.
- Many companies have dedicated teams focused on legal, regulatory, compliance, and policy matters. Your knowledge of data protection laws and privacy regulations will be highly valuable in these roles.
- Companies looking to expand into new markets or regions often require experts in data protection to navigate the complex web of international privacy laws.
- As a graduate with specialized knowledge, you may also have opportunities to join executive leadership or management teams, where you can provide strategic guidance on data protection and privacy concerns.
- Within the operations department, your skills can help streamline data handling processes, ensuring that data is managed securely and efficiently.
- Companies rely heavily on data for marketing and sales strategies. Your expertise can help these teams utilize data responsibly and ethically while staying compliant with privacy regulations.
- Tech companies, in particular, are always in need of professionals who understand data protection and privacy. You can work on building and maintaining secure systems and applications.
In addition to these opportunities, you can also consider entrepreneurial paths such as starting your own data protection consultancy or joining early-stage startups that require expertise in privacy management.
Your MBA with a specialization in Data Protection and Privacy Management equips you with the knowledge and skills to excel in a variety of roles and industries, making you a valuable asset to potential employers.
What kind of recruitment and placement support will I get?
- Unique Training Method: We're the sole organization in India offering comprehensive, exercise-based courses.
- Employer Recognition: Many leading employers, law firms, and companies actively seek our high-performing students.
- Career Opportunities: Success in our courses can lead to job placements, internships, and assessment internships in esteemed law firms, with renowned lawyers, and various companies.
- Empowering Learners: We focus on empowering learners with not just knowledge and skills, but also real-world opportunities.
- Dedicated Support Team: Our dedicated team is here to assist you with placements, internships, and freelance opportunities.
- Proven Success: Between April 2021 and June 2023, we've helped over 21,000 students secure job and internship opportunities.
- Media Recognition: Our achievements have been featured in respected media outlets like The Hindu, Business World, and India Education Diary.
- Impressive Value: Our students have secured over Rs. 2.7 Crore (USD 330,000) worth of work, with records of INR 30 LPA (USD 37,500) domestically and INR 50 LPA (USD 62,500) internationally.
- Comprehensive Support: From day one, our placement team guides you in setting goals, crafting standout CVs, enhancing interview skills, and supporting your critical first month on the job or during an internship.
- Trusted Recruiters: We've built strong collaborations with recruiters who prefer hiring our well-trained students.
- Competitive Edge: Partnering with us gives you an edge in the job market and opens doors to exciting career prospects.
How can you help businesses and clients after you obtain an international MBA degree with a specialisation in data protection and privacy?
You can help businesses and international clients with the following after you complete this course:
#1 - Data Protection and Privacy Management
- Ensure that an international organization is compliant with data protection laws in multiple countries
- Advise the management on applicability and implementation of laws for cross border transfer of data
- Implement a privacy strategy for a global organization, with local modifications for different jurisdictions
- Set up and manage a privacy team within the organization and liaise with internal and external stakeholders
- Perform all the functions of a data protection officer in-house or as an external consultant
- Conduct various privacy audits and assessments as an in-house leader or external consultant
- Lead the organization’s ISO 27001 certification initiative
- Implement technical, managerial and other controls for data protection, information security and privacy
- Deploy privacy by design framework
- Develop expertise at incident response and incident management
#2 - Leadership Outcomes
- Data protection and privacy management concerns at an organizational leadership level and roles of C-suite executives
- Reduce the workload of the top management team by assuming responsibility to solve difficult problems
- Provide leadership and contribute in conversations and meetings with seniors, top management, investors and other stakeholders, including customers and government
- Build a community and mobilise public conversation around a business cause or area of importance for the business
- Align your manager or a CXO to your vision and projects - with persuasive data
- Deal with conflict management within your team, across teams on a project and with a senior
- Transition responsibility and ownership to teams
#3 - Hiring, organizational expansion and growth
- How to manage data protection aspects of personnel planning and data and privacy challenges in high growth organizations
- Create a vision and mission statement for the growth of an organization
- Build high-performing teams for any business function in a remote environment
- Assist CXOs in hiring and engage international talent
- Learn how to implement technology and systems for a global and 100% remote organization - deploy OKRs, time tracking and project management tools for collaboration and measurement
- Create performance appraisal systems and growth paths for people to succeed in an organization
- Learn how to measure and deal with lack of performance adequately
#4 - International Business Expansion
- Understanding data protection and privacy management laws and regulatory regime around the world, and how it impacts international business expansion
- Analyze economic, political indicators and taxation regime for potential countries of expansion
- Structure the global business
- Analyze competitor landscape
- Negotiate international contracts
- Prepare presentations in international meetings keeping in mind the cultural norms and ethics of the participants
#5 - Operational Management, Finance and Strategy
- Data protection and privacy management for financial, fiduciary and management data
- Analyze the financials of a business:
- Profit indicators - Gross Profit, Net Profit, EBIT, EBITDA
- Balance Sheet Analysis
- Cash Flow Statements Analysis
- Basics of Cost Analysis
- Ticket Size, Average Revenue Per User (ARPU), Burn rate, Cost of Acquisition Per Customer (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Advice on possible strategies to increase ticket size, ARPU and CLV
- Identify competitive landscape - spot market gaps and opportunities and propose services/ products to fill the gap in a sector of your choice
- Prepare a strategy to launch an MVP covering the following
- Product Vision, Features and Design
- Team Requirements
- Launch and roll-out strategy - landing pages, marketing, ads + sales
- Delivery + Customer support requirements
- Customer satisfaction measurement method
- Make compelling proposals, brochures and presentations
- Budgets
- Execute the strategy:
- Assemble the team - create a virtual war room
- Write landing pages that convert
- Configure email marketing and social media ads
- Undertake performance measurement of marketing initiatives
- Create a Customer Onboarding Process
- Delivery and Support, Troubleshooting
- Learn how to address negative feedback and deal with Negative PR
- Optimise and create a Management Information System (MIS)
- Identify relevant functions and create KPIs for successful execution and delivery
- Identify KRAs for executives involved in delivery and support
- Create a comprehensive performance management system
- Create an NPS system to measure customer feedback
- Create appropriate reporting mechanisms
- Deploy an MIS
- Assist a business in creating a pitch deck and various other documents for funding:
- Pitch deck
- Historical financial documents of the business
- Business plan
- Financial plan and projections
#6 - Marketing and Social Media Initiative Deployment
- Data compliance in marketing and emerging challenges
- Identify important metrics for marketing and sales conversion
- Create a marketing funnel to move customers from awareness to conversion
- Contribute to copywriting and video creation initiatives for products and services
- Deploy strategies for organic engagement
- Learn how to measure the effectiveness of ad campaigns
Can I get remote freelance work after doing this course?
At LawSikho, we have two types of students: those who already possess good legal skills and those who are in the process of learning. We believe in enabling our learners to start earning from their knowledge without delay.
For students with professional-level legal skills, we offer opportunities in contract drafting, data & privacy, international business law, US immigration law, litigation support, and international IP law work, etc.
However, we understand that acquiring professional-level skills takes time. For those who are still developing their legal skills, we provide alternative work opportunities such as writing articles, conducting research, legal transcription, data entry, law firm administration, social media management, and more. Some students even engage in tasks like voice-over work, data compilation, translation, and virtual assistance.
We have established a dedicated team that actively pitches to organizations in the US to help LawSikho students find remote work.
We have set up a US entity to bridge the trust gap between US legal professionals and an organization operating from India.
We focus on getting learners their first three clients, guiding them in crafting impressive proposals. By the time they secure these initial clients, learners become well-adjusted to the process and can independently attract more clients.
They build their CVs and profiles with real work experience and testimonials, opening doors to numerous opportunities.
Getting started is often the hardest part, but at LawSikho, we make the process frictionless. We have witnessed law students earning well over $1000 per month.
Some students have earned $500 in their first month as a side gig. We have students who, after a year, now earn $10,000 per month. While some may start with $300, they make progress by learning new skills, improving their profiles, and pitching for higher-paying work.
Between April 2021 and June 2023, we created over 21000+ opportunities for our learners, resulting in thousands of students securing freelance work. The total value of work secured amounts to over $3,30,000 (Aprox INR 2.7 Crore). Additionally, hundreds of individuals found employment, and secured internships.
Please note that these numbers represent the initial gigs facilitated directly by us or those on which we actively collaborated with the learners. Students have also secured additional work beyond our tracking.
How will you clear my doubts and help me if I am struggling to understand or learn a concept?
- In our live classes, you can ask questions, share your screen, receive personal feedback, and have your doubts cleared.
- If you need more help after getting feedback on an assignment or want career advice, you can schedule a private one-on-one call. Our evaluators and mentors are here to assist you and give you advice that's tailored to your needs.
Degree Certification
The degree awarded will be an MBA in Data Protection and Privacy Management from the Swiss School of Management.
It is a 15 months course that can be completed within 30 months to be eligible to receive the completion certificate (Degree).
The SSM MBA Degree is fully accredited by IACBE and CHEA-Council for Higher Education. SSM MBA degree is also accredited by the Department of Veterans Affairs in the USA. SSM is a quality certified school by EduQua, the Swiss Quality Certification label (accredited by the Swiss Federal Government) for Institutions of higher and continuous education.
Sample Degree

Core Subjects
Globalisation
4 ECTS
- This course focuses on and facilitates further discussion of the implications of globalisation for businesses and investigations of the primary economic dimension connected with the proliferation of globalisation.
- The main objective of this class is to familiarise students with ideas, concepts, and ways of analysing globalization as well as the encouragement of thinking about the future agenda for global leaders in such a changing environment.
Goals of the Course
- Identify and discuss the major economic, political and social ties that comprise contemporary global interdependence
- Develop an understanding of the vast impact globalization has on varied industries such as - the rise of transnational corporations and global commodity chains, to global health challenges and policies, to issues of worker solidarity and global labour markets, through to emerging forms of global mobility by both business elites and their critics
- Discuss the trajectory globalization has taken, and begin to consider new directions for globalization and society
- Enter the global dialogue that is a product of globalization.
- Recognize and understand the basic concepts of globalization and its interaction with the world we live in.
Assessment Details
The assessment for this module is based on one assignment. Paperwork (3,500 words +/- 10%)
Leadership 360 Degrees
4 ECTS
Scope:
- The objective of this course is to help students acquire and develop skills in relation to effective leadership within organizations.
- Students will understand and compare different approaches, theories and methodologies about leadership and will practice leadership behaviours through class exercises and assignments.
Goals of the course:
- Understand the principal components of a leader’s contribution to high-performance working
- Understand the different ways leadership has been defined, assessed and appreciated in the academic and managerial context
- Practice different behaviour indicators related to leadership skills in a working environment
- Evaluate elements of key leadership and management theories and translate theoretical constructs to practical applications
- Have a personal development plan, which includes the development of key leadership behaviours.
- Are able to create practical strategies for leading down, across, and up in your specific situation
- Are able to Instill a culture of 360° leadership within their organization.
Accounting & Financial Management
4 ECTS
- In this module, students are introduced to key elements of finance and accounting enabling them to draw essential conclusions on an organisation’s performance and also with reference to the stakeholder and in particular shareholder satisfaction.
Goals of the course:
- Critically evaluate the informational content of financial and accounting reports and their use as a tool for appraising corporate performance.
- Develop an understanding of financial planning tools and techniques and the contribution they make to the achievement of an organisation’s core objectives.
- Evaluate the results of financial models used for long-term decision-making.
- Develop confidence in using financial terms and language necessary for effective senior management.
International Business Law (LAW555 - Part 1)
2 ECTS
Scope: This Module is designed to equip students with International Business Law concepts and covers the main topics in this field, such as:
- the settlement of disputes,
- the Multinational Organization,
- Foreign investments Laws and Codes, as well as legal issues arising out among businesses in the cross-border context.
- International contract law,
- conflict of laws, i.e. in case of insolvency,
- international private dispute resolution,
- choice of foreign law (the Governing Law), and
- the basic elements of E-Commerce.
- The Module will help international affairs and other non-law students to have a general understanding of international business law so that they are better placed to understand the underlying legal environment in international economic affairs.
- In addition, this Module will review and discuss a number of chapter questions and cases in brief, as well as certain Court decisions, treaties resolutions and other international legal instruments of importance.
Goals of the course
- understand general concepts of international business law;
- identify and locate main sources and authorities of international business law;
- read and interpret basic international business law provisions;
- apply international business law provisions to fact patterns and real-life scenarios
The module is organized into eight blocks:
- Introduction to International Business Law, the International Legal system. Assignment.
- International conflict of Laws. The settlement of disputes through diplomacy; Case study/Assignment
- The Multinational Enterprise: strategies for doing business globally. E-Commerce; Case study/Assignment
- The regulation of international contracts; cross border insolvency; case study & assignment
- The international contract: issues and particular clauses; case study/Assignment
- The Joint-Ventures: structure, powers and responsibilities; Study Questions
- Drafting, execution and performance of international contracts; representations, warranties and financial covenants; the U.S. Law on Bankruptcy. Study questions
- Final Exam
The assignment is for each aspect of the module
Business Ethics (LAW555 - Part II)
2 ECTS
The goal of the course
- Understand the issues addressed under the terms “business ethics” and “corporate social responsibility”
- Understand the moral dimension of business
- Understand the key principles of managing the responsibilities of doing business
- Be able to understand and analyze the managerial role in managing responsibilities and expectations
- Build on the moral quality of business to strategically mobilize the various relationships with stakeholders.
Assessment Details
The textbook is divided into two sections: theory and application. For each section, you will write an essay of 3000 words.
Global Macroeconomics & International Finance
4 ECTS
Scope
- In this module, students are introduced to theoretical models about the microeconomic foundations and the macroeconomic consequences of financial markets and globalization. A particular focus will be made on globalization and the role of macroeconomics.
Topics include:
- overview of macroeconomics;
- measuring gross domestic product,
- inflation and unemployment;
- demand including the multiplier process;
- supply, business cycles, long-term growth;
- money, banking and monetary policy;
- inflation;
- interest rates;
- stagflation;
- deficits and fiscal policy;
- exchange rates, and balance of payments;
- exchange rate policy;
- purchasing power, and
- interest rate parity
Goals of the course
- The concepts and measurement of gross domestic product, unemployment, and inflation.
- The difference between business cycles and economic growth and the factors that contribute to each.
- The concept of how Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply determine equilibrium price and output in the short-run and long-run.
- The concepts, tools, and implementation of fiscal policy.
- The concepts, tools, and implementation of monetary policy.
- The concepts of Comparative Advantage, the balance of payments and its components, and the determinants of exchange rates.
Assessment
The assessment for this module is based on one assignment. Find the currency of your home country and describe its value relative to the USD. If you are a U.S. citizen choose China, Japan, or the Eurozone (a country using the Euro). Is it under or over-valued compared to the USD? What problems or benefits do you think this relationship might cause for your country? Why? Governments often intervene (manipulate) in foreign exchange markets to give their currency a more favorable rate. Do some research on the web to see what intervention has occurred or has been discussed lately regarding your country’s currency. Essential for the assessment is the depth of the work, the logic (e.g., cause and effect) and a high level of critical reflection.
Paperwork (3,500 words +/- 10%)
Negotiating Globally [Cross Cultural Management]
4 ECTS
Goals of the course
- Explain the cultural, contextual and personal factors that influence interactions within multinational companies.
- Explain how your personal and cultural values and behavioural preferences when working in a team environment impact your ability to function and manage effectively in a cross-cultural business environment.
- Diagnose personal, contextual and cultural factors that help or hinder multicultural team effectiveness in teams in which you personally work.
- Deliver a logically constructed persuasive presentation using appropriate visual aids.
- Articulate ideas, decisions, recommendations and other information in a clear, concise writing style tailored to a given audience.
- Demonstrate the ability to work effectively with others to complete a group project
Objective
- In this Module and in the book, we look at cultural differences and how they affect the processes of doing business and managing.
- The Module consists of short movies that introduce the topics per chapter, while each chapter on the platform covers a chapter in the handbook and is accompanied by slides, multiple-choice questions by way of self-test and graded essay questions.
- In this module and this book, we examine the visible and invisible ways in which culture impacts on organizations. Then we have to explain what we mean by “culture”: the way in which a group of people solves problems.
- The characteristic of this Module is that culture is studied as a dynamic.
Assignment Details
The textbook is divided into twelve chapters. For each chapter, you will write an essay of 1500 words.
Organizational Behavior [OMB555 - Part II]
2 ECTS
Scope
- This module covers a range of models and theories, which are explaining more than moral and ethics in business activities.
- Organisational behaviour and corporate social responsibility are highly practical.
- They have much influence on an organisation’s competitiveness and the market acceptance of its products.
Goals of the course
- Define organisational practices with regard to ethical corporate behaviour.
- Identify and analyse best practice examples of good corporate citizenship with a particular emphasis on the responsible organisation.
- Understand models and frameworks in the field of Corporate Social Responsibility.
- Develop ethical standards for their own work as managers.
- Improve organisations’ approach to sustainable management and benefits for economy and society.
Human Resource Management [OMB555 - Part I]
2 ECTS
Scope
- This Module that focuses starts from a strategic perspective. The management of human resources is consistently discussed in relation to the achievement of strategic goals.
- For that reason, this Module has several chapters that focus on particular contexts for strategy, such as types of industry.
- In this Module the topics that are discussed are treated in a practical manner, allowing the student to apply what is learned to his or her practical needs.
- The Module consists of documents that introduce the topics per chapter, while each chapter on this platform covers a chapter in the handbook and is accompanied by slides, multiple-choice questions by way of self-test and graded essay questions.
- In this Module and with the use of this book we examine the importance of Human Resource Management for the business organization, in relation to its strategic role.
- What is unique about this Module is that it has a strategic perspective on human resource management. That means that it consistently presents the strategic choices that have to be made in order to optimally manage the human potential towards achieving the goals of the organization.
Goals of the course
- Contribute to the development, implementation, and evaluation of employee recruitment, selection, and retention plans and processes.
- Administer and contribute to the design and evaluation of the performance management program.
- Develop, implement, and evaluate employee orientation, training, and development programs.
- Facilitate and support effective employee and labour relations in both non-union and union environments.
- Research and support the development and communication of the organization's total compensation plan.
- Collaborate with others, in the development, implementation, and evaluation of organizational and health and safety policies and practices.
- Research and analyze information needs and apply current and emerging information technologies to support the human resources function.
- Develop, implement, and evaluate organizational development strategies aimed at promoting organizational effectiveness.
- Present and evaluate communication messages and processes related to the human resources function of the organization.
- Manage own professional development and provide leadership to others in the achievement of ongoing competence in human resources professional practice.
- Facilitate and communicate the human resources component of the organization's business plan.
- Conduct research, produce reports and recommend changes in human resources practices.
Examination Details:
The textbook is divided into three sections. For each section, you will write an essay of 2.000 words.
Content & Assignments For Application to Data Protection and Privacy Management
- Create a plan to upskill and sensitize Human Resources Team on Data Protection and Privacy
- Onboard HR as a key internal player for implementation of the organization’s privacy and data protection vision
Competitive Strategy
4 ECTS
Scope
- This course introduces students to the subject of strategy and helps them better understand the overall impact of internal and external influences on the firm.
- The basic purpose of the course is to provide the student broad insights into the practice of strategic management, and its real significance in contemporary multi-national corporations.
Goals of the course
- Understand how industry structure and environmental trends help determine competitive advantage for firms
- Explain the different forms of strategy
- Identify the nature of and triggers of strategic change.
- Assess the resources and capabilities of a firm
- Analyze the external environment of a firm
Assessment Details
The assessment for this module is based on one assignment. Students will develop a report on the investment management of an organisation. This can either be an organisation of his or her own choice or one, which is selected by the module tutor.
In this report to the senior management, students will develop and suggest solutions for a specific problem being typical in investment. Based on relevant theoretical underpinning (incl. appropriate academic literature) the report will analyse the problematic, select and differentiate among a variety of options and will recommend (a) solution(s).
Essential for the assessment is the depth of the work, the logic (e.g., cause and effect) and a high level of critical reflection. Paper work (3,500 words +/- 10%).
Content & Assignments For Application to Data Protection and Privacy Management
- Identify ways to use data protection, information security and privacy management as a competitive advantage in a global market
Investment Management
4 ECTS
Scope
- The course is designed to teach investing techniques, principally for publicly traded securities (although similar principles apply to private markets).
Topics include:
- the function of financial markets,
- analysis of risk and return,
- analytic tools, valuation of financial assets: stocks, bonds, options;
- investigative and research techniques, such as reading 10K’s, and other public filings for an opportunity;
- valuation methodologies;
- qualitative investigative techniques such as talking to company management
- Long term financial planning, wealth management and personal finance also taught.
Learning Objectives
- Learn to invest effectively considering risk/return parameters.
- Develop a keener understanding of financial market operations and make more informed risk/reward decisions.
- Understand operational modes of different investment vehicles: mutual funds, private equity, hedge funds, etc.
- Invest more profitably: increase risk-adjusted investment returns, minimize investment losses, and operate more effectively financially overall.
Assessment Details
- The assessment for this module is based on one assignment. Students will develop a report to the investment management of an organisation. This can either be an organisation of his or her own choice or one, which is selected by the module tutor.
- In this report to the senior management, students will develop and suggest solutions for a specific problem being typical in investment. Based on relevant theoretical underpinning (incl. appropriate academic literature) the report will analyse the problematic, select and differentiate among a variety of options and will recommend (a) solution(s).
- Essential for the assessment is the depth of the work, the logic (e.g., cause and effect) and a high level of critical reflection. Paperwork (3,500 words +/- 10%)
Strategic Marketing & Social Media Planning
4 ECTS
Scope
- This module explores the role of marketing in a variety of contexts including services, new technology and social media.
- Adopting a strategic focus, the course will critically review current theory and practice and discuss how marketing strategies are evolving in the light of changes arising from increasingly sophisticated and demanding consumers, social media technology and globalisation.
- Marketing and social media are an inseparable pair. The digital world today is simply the world: but with new rules, codes, languages and dynamics. The countries that populate this 2.0 world are called social channels.
- Being on Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, Linkedin and YouTube means opening your micro-universe to the infinite one of opportunities and exchanges. The module aims to deliver knowledge and ability to students allowing them to build their own network of professional contacts to optimize relationships, exchanges and sales and it provides an opportunity to apply previous knowledge in marketing through case studies and projects.
Learning Objectives
At the end of this module students will be able to:
- Engage in strategic thinking including projecting future outcomes, setting goals, and reflecting on the implementation process to reach those goals;
- Integrate marketing theory, prior practice and prior learning into the strategic marketing environment;
- Communicate effectively in oral and written forms about marketing strategy using appropriate concepts, logic and rhetorical conventions create profiles on all platforms;
- Use multimedia platforms and suites;
- Know and interpret the main KPI metrics;
- Perfecting the use of image-editing apps
- Understanding how to set up an advertising campaign on Facebook, Google, Twitter;
- Fully evaluate the rules of image semiotics and new media;
- Analyze with effective tools the competence, reliability and depth of a content writer for social channels; and
Choose which social channels to set up your campaign with and start it independently.
Assessment details
The assessment for this module is based on one assignment. Students will develop a report to the senior management of an organisation. This can either be an organisation of his or her own choice or one, which is selected by the module tutor.
In this report to the senior management, students will develop and suggest solutions for a specific problem being typical in marketing. Based on relevant theoretical underpinning (incl. appropriate academic literature) the report will analyse the problematic, select and differentiate among a variety of options and will recommend (a) solution(s).
Essential for the assessment is the depth of the work, the logic (e.g., cause and effect) and a high level of critical reflection. Paperwork (3,500 words +/- 10%).
Content & Assignments For Application to Data Protection and Privacy Management
- Ensure that your social media plan for marketing activities is compliant with global data protection norms
Management in Digital Economy
4 ECTS
Scope
- The objective of this course is to provide the students with knowledge and competencies on using integrated and system solutions in advancing the management to the requirements of the Digital Economy.
- In this course, students will learn how to adapt management, its strategies and functions to smart and sustainable solutions that the 2.0/4.0 era has brought to enterprises.
- By the end of this module, you’ll have a richer understanding of both successful and unsuccessful digital transformations and know what strategies are more successful than others, and you’ll have a sharper sense of digital innovation and be able to approach such management from a more informed, digitally-oriented point of view.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this module, students would be able to:
- Define and assess internal and external driving factors for digitization and position them in strategy and business model;
- Use strategic analysis tools to understand internal and external determinants influencing the company performance and propose improvements with different approaches;
- Have the basic knowledge on Information Technology which enabled and is still enabling the innovation of enterprises and the whole market.
- Be familiar with digital economy terminology and able to communicate and present digital plans;
- Demonstrate entrepreneurial attitude towards i4.0 opportunities for business.
Research Methodologies
4 ECTS
Scope
- This module offers students profound insights into empirical research with a particular focus on business research.
- Sound methods of gathering data, their empirical evaluation and assessment by research scrutiny deliver a sound design and structure.
- In addition, this module introduces research strategies and acknowledged methods constituting what makes reliable and valid studies.
- This module will further guide students towards the sound design of their thesis.
- Students will have to develop a planning and prepare their thesis by reflecting on the advantages and disadvantages of particular research strategies, analyse the requirements involved in the research process, and demonstrate their understanding of empirically valid and reliable research, which is presented in the thesis research proposal (practice-oriented, applied research) with tutors’ support.
Module Learning Objectives
Students should be able to:
- Demonstrate their knowledge of the need for a defensible fit between the nature of practice-oriented problems in empirical research and its methods of inquiry investigating those problems and of means for securing the essential fit
- Be capable to select between different designs for addressing a research problem and be mindful of central distinctions in data collection, analysis & reporting
- Be capable of applying tests of quality & appropriateness to different research proposals and designs
- Demonstrate an awareness of research methods and their potential impact on the reception afforded to research efforts
Assessment Details
The assessment for this module is based on two assignments.
1. Essay (3,500 words)
The essay will investigate and contrast different research methods. Essential is a critical appraisal of one or more given question(s) in which a solid understanding of research methods has to be demonstrated. It is essential that students critically discuss the advantages and disadvantages, but also limitations of each method with a particular focus on research in a business-related context.
Criticality, depth of discussion and contrasting argumentation are key for the assessment.
2. Thesis Proposal (1,500 words)
Based on the module’s learning outcomes students are requested to elaborate their individual thesis proposal. In this proposal, they will present a precise research strategy and justify the value of their thesis with reference to modern management and a particular eye on questions of sustainability and ethics. The thesis proposal is not assessed by a mark but has to be approved by a member of the faculty. This approval decides on a student’s admission to the thesis.
Content & Assignments For Application to Data Protection and Privacy Management
Create an internal privacy program to obtain consent for obtaining and processing data and protect privacy for empirical research initiatives
Subject-wise Division of Credits
|
No. |
Subjects |
Category |
Credits (No. of ECTS) |
|
1 |
Global Macroeconomics & International Finance |
MBA |
4 |
|
2 |
HRM & Organizational Behaviour |
MBA |
4 |
|
3 |
Accounting & Financial Management |
MBA |
4 |
|
4 |
Investment Management |
MBA |
4 |
|
5 |
Strategic Marketing and Social Media Planning |
MBA |
4 |
|
6 |
Competitive Strategy |
MBA |
4 |
|
7 |
Globalization |
MBA |
4 |
|
8 |
International Law & Ethics |
MBA |
4 |
|
9 |
Management in Digital Economy |
MBA |
4 |
|
10 |
Leadership 360- Degrees |
MBA |
4 |
|
11 |
Negotiating Globally |
MBA |
4 |
|
12 |
Research Methodologies |
MBA |
4 |
|
13 |
Thesis |
Specialisation-focussed |
12 |
|
14 |
Relevance of Data Protection and how to deal with data theft, data leaks and breach of privacy |
Specialisation- Module 1 |
4 |
|
15 |
EU - EU GDPR |
4 |
|
|
16 |
Managing Contracts and Litigation under GDPR |
2 |
|
|
17 |
Data protection laws in the US: Federal and State laws |
Specialisation - Module 2 |
4 |
|
18 |
Data Protection law in Canada |
2 |
|
|
19 |
Data Protection law in South East Asia |
2 |
|
|
20 |
Data Protection Regime: Middle East and India |
2 |
|
|
21 |
Privacy Management by Businesses and How to Create a Privacy Program of a Global Organization |
Specialisation - Module 3 |
6 |
|
22 |
How to implement a “privacy by design” framework |
4 |
|
|
TOTAL |
90 |
||
Concentration/Specialization Subject: Data Protection and Privacy Management
Relevance of Data Protection and how to deal with data theft, data leaks and breach of privacy - 4 ECTS
Legal basis for enacting data protection legislations
- Why is data sought to be legally protected?
- Which data is sought to be protected?
- Overview of global data protection regimes in US, EU, South East Asia & Africa
- Important themes in data protection regimes across the world
- Do local companies need to care about offshore data protection laws? Why?
Consequences of data protection violations
- Exorbitant Domestic and Cross border Fines
- Third-party indemnity claims
- Reputational consequences
- Inability to secure new business
Types of data collected and processed by business for commercial and other purposes
- Personal data and its subcategories
- Sensitive personal data
- Transaction-related data and preferences
- Anonymized/ pseudonymised data
- Business entity-related data
- Economy related data
Data-driven business models and classic data protection scenarios:
- Social Media
- E-commerce
- Services aggregators
- Search Engines
- Content aggregators
- Rating and review business
- Data intermediaries
- Datacentres
- Marketing and sales agencies
- Data intelligence businesses
Data-intensive industry sectors: BFSI, Retail, E-Commerce, Healthcare, Education, Software As a Service (SAAS), Consulting, Real estate, infrastructure and smart cities, Media and entertainment, Law and justice, pharma, advertising, supply chain and logistics, security and defence, agritech, R&D
Data flow and data sets collected by key business functions:
- Finance
- HR
- Product development
- Marketing
- Sales
- Customer support
- Strategy
How to create a personal data analysis form
How to map data flow - internally or as external consultant
- Involvement of functions in mapping data flow
- Recording the source of data, use of data, storage of data by the functions
- Drawing or noting the movement of data and identifying unintended uses
- Noting the locations, transfer methods, applicability of law
- Identifying the ‘need for data’ and accountability at each stage of movement
- Identifying and installing safeguards to prevent leaks and unintended uses at each stage
How to create a personal data asset inventory list
How to create a data protection assessment report as an external consultant (EU GDPR basis)
How to create a project implementation plan (EU GDPR)
How to analyze data protection law of any country
- Personal data vs. sensitive personal data
- Consent of a ‘data subject’
- Rights of a data subject
- Principles/ criteria for processing data
- Provisions for security of data
- Data portability and transfers
- Duties of controllers or their equivalent authority in national law
- Data Processors and their obligations
- Breaches and their categories
- Responsibilities in case of breach
- Provisions for data protection impact assessments
- Authorities under the data protection law
- Penalties for violation
Data Sovereignty, Data Residence and Data Localisation and Its Impact on Businesses
- Data Sovereignty vs. Residence vs. Localisation
- Reasons for enacting data localisation legislations by countries
- Commercial and tax implications for businesses impacted by data localisation requirements
- Data Residency as a Service
- US - China and US - India controversy on data localisation
- Chinese data localisation requirements under various legislations and administrative measures
- Russia’s On Personal Data Law
- Indian Personal Data Protection Bill
- Regulation by Reserve Bank of India
- Examples of data localisation prohibition: US-Mexico-Canada (USMCA) and US Japan Agreement on Digital Flows
- SOC 2 & PCI DSS standards
Popular causes of data leaks and incidents and how to avoid them
- Categories of data breaches
- Weak and Stolen Credentials, a.k.a. Passwords
- Back Doors, Application Vulnerabilities
- Malware & Ransomware attacks
- Social Engineering
- Too Many Permissions
- Insider Threats, e.g. unauthorised access, unauthorised use and misuse of data by employees and vendors
- Physical Attacks
- Improper Configuration, User Error
- Absence of cyber security mechanisms
- Negligence in data protection
- Lack of appropriate internal controls relating to data access
- Old and vulnerable systems
Preparatory work for handling data breaches
- Implementation of a robust data breach notification procedure
- Preventive measures
- Policies for privacy, data retention and data use
- Data Protection Addendums with processors
- Privacy awareness training for relevant employees and the Board
- Contractual indemnities
- Insurance
Use of block chain AI in data protection
How to handle a data breach
- Security incident management policy
- Security incident response team
- Annual Reports
- Mandatory notification to controller and regulatory authorities
- Post breach investigations
- How to raise indemnity claims
- International commercial arbitration proceedings for data breach indemnity claims
Template:
- Format for personal data breach notification
- Data breach notification form to supervisory authority under EU-GDPR
- Data breach notification form to data subjects under EU-GDPR
- Binding corporate rules under EU-GDPR
How to create Rock Solid Incident Response Plans:
- Role of a DPO in a data breach
- Use of an incident ‘triage matrix’
- 7 phases for incident response: Preparation; Identification & Scoping; Data Access Security; Containment & Intelligence Gathering; Eradication; Recovery; Follow up/ review
- Role of various organizational actors: Security Operations Centre (SOC), Incident Manager, CIRT team & Threat Intelligence Team
- Role and interfacing with internal stakeholders CEO, CISO and various C-levels, IT, Legal, DPO, public relations/marketing, chief customer officer, vendor manager, Compliance, HR/internal comms, Board directors
- Role and interface with external players: Police, PR agency, law firm, IT forensics, insurers
Template:
- Sample incident response plan
Data protection in the EU: EU GDPR - 4 ECTS
EU GDPR
Introduction to EU GDPR
- Applicability
- Participants under GDPR
- Requirement to create a supervisory authority
- Responsibility of the supervisory authority
- Core principles of GDPR
Data protection officer and data protection authority
How are Governments expected to deal with protection of data under GDPR?
- Reconciling right to freedom of expression with right to protection of personal data
- Reconciling public access to official data with right to protection of personal data
- Processing of national identification numbers
- Provision of specific rules for processing of employment related data
- Processing of data in public interest or for scientific or historical research or statistical purposes.
How to implement changes to key business functions to implement GDPR compliance\
- Product development
- Technology
- Marketing
- Sales
Consent under GDPR
- How to obtain consent of a data subject
- How to draft a privacy notice
- Difference between a privacy policy and a privacy notice
- How to draft a Data Protection Addendum to the Terms of Use of a Website
- How to draft a Data Protection Addendum for third party technology service providers
Lawful processing under GDPR
- Purposes for processing data
- Cross-border data transfers
- How to draft a data processing agreement
- Data adequacy decisions
- Schrems I and Schrems II
Responsibilities of data processors and data controllers
Rights of customers, employees and other “data subjects”
- Right to be informed
- Right of access
- Right to rectification
- Right to erasure
- Right to restrict processing
- Right to data portability
- Right to object
- Rights related to automated decision making
When and how to conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment
- Understanding various customer scenario descriptions
- Personal data analysis form
- Asset inventory list
- Project implementation plan
Sanctions and consequences of non-compliance with GDPR
Checklists:
- Checklist for implementing GDPR compliant data protection systems
- GDPR checklist for Data Controllers
- GDPR checklist for Data Processors
- GDPR checklist for transfer of data outside EU
- Checklist of documentation required to be maintained under GDPR
Data Protection in UK post Brexit: UK Data Protection Act, 2018 vs. EU-GDPR
- Privacy impact assessment
- Consent mechanisms
- Bases for processing data
- International data transfers (Within EU vs. Outside EU)
- Breach notification procedure
Templates:
- Personal data protection policy
- Privacy notice/policy
- Employee privacy notice
- Data retention policy
- Data subject consent form
- Parental consent form
- Data processing agreement
- Standard contractual clauses
- Record of processing
- Right to erasure request form
Managing contracts and litigation under GDPR - 2 ECTS
Requirements under GDPR and other laws to enter into legal contracts
Common Data Protection Agreements and review work
- Outsourcing (Controller-Processor) Agreements
- How to review terms and conditions of use of websites
- How to review privacy policies so they are compliant with data protection laws
- Addendums
Data processing concerns in Healthcare, BFSI, E-commerce, Social Media, SaaS
Assessing impact of new data protection regulations
- How to keep tab of constant legislative changes
- Drawing up impact assessment reports
- Developing or amending contract templates accordingly
Managing data protection disputes and litigation
- Why is litigation management required?
- Preventing litigation
- Providing for litigation costs
- Status reports to management
- Different types of legal proceedings in data protection
- Complaints with Data Protection Authorities
- How to deal with a complaint filed against your organisation
- Complaints with Data Protection Authorities
- Damages claims
- Material or immaterial damage
- Extent of compensation
- Precedents and court decisions on compensation
- Collective and representative actions
- Injunctive relief
- Claims under competition law
Data protection laws in the US: Federal and State laws - 4 ECTS
Federal Laws:
- The Privacy Act of 1974
- The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
- The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA)
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- The Video Privacy Protection Act (VPPA)
- The Telephone Consumer Protection Act
- The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act
Data protection laws of some important US states:
- California: California Consumer Privacy Act
- New York: New York Privacy Act, The New York SHIELD Act
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts General Laws
Major requirements under US State laws:
- Notice requirements
- Access to records and data
- Uses and disclosures
Data protection authorities and regulators in the US
- Federal Trade Commission
- The Department of State’s Privacy Office
- Privacy Unit of the Department of Justice
Data Protection Law in Canada - 2 ECTS
Basic principles of data protection law in Canada
- Accountability
- Purpose of use of data
- Consent
- Limiting collection, use, disclosure and retention
- Accuracy
- Openness
- Ensuring safeguards
- Compliance
Overview of the Data Protection Regime in Canada: Federal Laws
- The Personal Information and Protection of Electronic Documents Act
- Bill C11 - The Digital Charter Implementation Act, 2020
- The Consumer Privacy Protection Act
- The Personal Information and Data Protection Tribunal Act
- Electronic Documents Act
Overview of the Data Protection Regime in Canada: Provincial Laws
- British Columbia: Personal Information Protection Act
- Alberta: Personal Information Protection Act
- Quebec: Act Respecting the Protection of Information in the Private Sector
- Ontario: FIPPA / MFIPPA / PHIPA / CYSA
Data Protection Authorities in Canada
- Office of the Privacy Commissioner
- Competition Bureau of Canada
- Data Protection Tribunal
Data Protection Law in South East Asia - 2 ECTS
Data protection and privacy regulation in Singapore
- Personal Data Protection Act 2012
- Info-communications Media Development Act, 2016
- Different Notifications, Rules and Regulations for Personal Data Protection
- Personal Data Protection Commission and Advisory Committee
Data protection and privacy regulation in Hongkong
- Basic principles of data protection and privacy in Hongkong
- Collection purpose and means
- Accuracy and retention
- Use
- Security
- Openness
- Data Access and correction
- The Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance
- Office of the Privacy Commissioner for Personal Data, Hongkong
- Guidelines and Practice codes on various matters such as identity cards, credit data etc. by the Office of the Privacy Commissioner
Data protection and privacy regulation in Philippines
- Republic Act 10173: Data Privacy Act of 2012
- National Privacy Commission
- Circulars, Advisories, Commission decisions and resolutions
Data Protection Regime: Middle East and India - 2 ECTS
Data Protection Regime in UAE: Dubai & Abu Dhabi
- Criminal Offences covered in the Penal Code relating to publishing or unlawful disclosure of personal data
- Articles of Federal laws penalising certain acts of data breaches such as intercepting phone calls, illegally accessing websites
- Federal Law governing collection, processing and transfer of healthcare data
- Regulatory Framework for Internet of Things (IoT)
- Laws applicable within the Dubai International Financial Centre: Data Protection Law DIFC Law No. 5 of 2020
- Laws applicable within the Abu Dhabi Global Market: Data Protection Regulations 2021
Personal Data Protection Bill of India
- How to prepare for compliance with the Personal Data Protection Bill
- Transition plan for existing businesses and cross border contracts once the bill is passed the impending Personal Data Protection Act on cross border contracts and agreements
- Rights of a data ‘principal’
- Obligations of a data ‘fiduciary’
- Conditions for obtaining valid consent
- Exemptions from consent
- Requirement of data protection impact assessments and audits
- Duties of a data protection officer
- Special provisions for processing data of children
- Restrictions on transfer and processing of data outside India
- Exemptions from compliance
- Powers of Data Protection Authority
- Personal Data Protection Bill vs. other data protection legislations such as EU GDPR
Templates:
- Organization-level privacy policies
- Privacy notice
- Audit template for independent auditor
Privacy Management by businesses and how to create a privacy program for an organisation - 6 ECTS
Overview of the privacy function of an organization
- When and which companies need a privacy function
- What is the work performed by the privacy team of a company?
- How to design the organization’s privacy vision and mission statement
- Privacy governance models - centralised and decentralized, CPO/ Core Model vs. Working Group Model
- Structure of a privacy team: Chief privacy officer (CPOs), privacy managers, privacy analyst, business line privacy leaders, incident response and security computer incident response team, Data Protection Officers (DPOs)
- Reporting structure of the DPOs and the CPO
- Common designations of privacy and information technology personnel in a company
- How to create the privacy strategy of a company
Key Responsibility Areas (KRAs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of persons in privacy and information security-related roles
- Chief Privacy Officer (CPO),
- Data Protection Officer (DPO),
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) and Chief Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Privacy Director
- Regional data protection leads or officers/ specialists, e.g. data governance specialist, incident response specialist
- Privacy or Information Security Manager
- Privacy Officer/ Privacy Counsel/ Legal specialist
- Privacy Engineers
- IT Compliance Officer/ Associate
- Data Security, Information Security and Privacy Engineer/ Analyst/ Specialist/ Advisor
- Risk & Compliance Consultant - Data Protection & Privacy
Example: Privacy Engineer JD (software developer)
- develop technical solutions to help mitigate privacy vulnerabilities
- analyze “software designs and implementations from a privacy and UX perspective,
- research, document, and help remediate design decisions, operating procedures, or processes that may directly or indirectly contribute to future privacy risks
- create cutting-edge privacy feature prototypes
- Help an organization lead better on privacy by example
- Partner with key business, technical and legal stakeholders across various business groups to implement Privacy by Design
How to deploy privacy knowledge in engineering roles?
- Front-end engineers
- Back-end engineers
- Product managers
- Technical Program managers
- Data scientists
- Engineers working in AI & ML teams
- UX developers
When to appoint a DPO
- Skillsets of DPOs
- In-house vs. external DPOs
- Responsibilities of DPOs
- Performance measurement mechanisms for DPOs
How to succeed as a Data Protection Officer (DPO) in an organization
- Duties of DPOs:
- Audits and Assessments,
- Processing of Data,
- Controls
- Transfer of Data,
- Incident Management
- Important clauses in a DPO contract with an external DPO
- How to identify conflict of interest
- Role of a DPO in the first month
- Meetings with top management
- Meetings with key business teams
- Review of policies and documents
- Review/ creation of assets and IT systems and infrastructure
Elements of Privacy program scope/ charter
- Business teams and their requirements,
- Global and local laws, regulations and standards driving compliance,
- Risk tolerance levels, cultural expectations and perspectives - values regarding privacy,
- Types of personal information collected, stored and processed,
- Regulatory changes that need to be observed (for example in USA, this would be state law changes),
- Privacy challenges
Creation of a cross-functional privacy strategy for organizational alignment
- Business alignment of goals
- Data governance of personal information
- Procedures for handling inquiries or complaints
- Automation and use of privacy apps
Creation of a privacy framework
- Laws and regulations
- Canadian Personal Information Protection and Electronics Documents Act
- APPs - Australian Privacy Principles
- EU-GDPR - European General Data Protection Regulation
- EU-U.S. - Privacy Shield
- US statutes such as CCPA, HIPAA - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, etc.
- CNIL, France’s Commission
- India’s Personal Data Protection Bill
- Law of other countries
- Principles, standards and guidelines
- Fair Information Practice (FIPS),
- OECD’s Protection of Privacy and Transborder Flows of Personal Data,
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) privacy task force and Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP),
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA),
- APEC Privacy Framework for Asia-Pacific data transfers
- Binding Corporate Rules
- How to create a compliance roadmap or plan
- Creation of implementation roadmaps from a compliance plan
- How to draft Binding Corporate Rules and get them approved
- Organizational communication plan to ensure continuous alignment to laws and regulations
Samples of Binding Corporate Rules:
- eBay with the Luxemburg DPA as the lead
- First Data with the UK ICO as the lead DPA
- HP with the CNIL as the lead DPA
- Intel with the UK ICO as the lead DPA
- JPMorgan Chase with the UK ICO as the lead DPA
- Philips with the UK ICO as the lead DPA
- Workday with the Irish DPC as the lead DPA
Privacy Program activities
- Privacy By Design to ensure privacy protection at every stage of product development
- National Institute of Standards and Technologies framework for privacy in engineering and risk management in federal systems
- AICPA and CICAs WebTrust
How to conduct Privacy Impact Assessments under various laws
How to create a data map for your privacy program
- Relevance of a data map
- Cost of not creating a data map
- Components of a data map
- Data use
- Data sharing
- Data storage
- Data retention process and policy
- Countries where the data is collected
- Countries to or between which data is transferred
- Identification of third-party data access points
Implementation of privacy trainings
- Statutes which require mandatory trainings
- Benefits of a privacy training
- Frequency of trainings
- Components of a training program: applicable law, internal policies, recognition of violations, addressing privacy complaints and misconduct, reporting procedures and escalation, consequences of violation, acknowledgement of completion of training and records maintenance
- Creation of an on-demand training program
- Reminders and refresher programs
How to monitor ongoing compliance with the privacy program
- How to conduct a privacy audit
- Confirmation of existence and compliance with internal controls, policies, and procedures
- Identification and rectification of compliance gaps
- Internal or external audits such as GDPR Audit or GDPR Assessment Report
- Rectification of audit gaps
- How to use privacy compliance tools such as “One Trust”
How to upgrade and amend the privacy program
- Changes to business - product segments or geography
- Changes in applicable law and regulations
- Changes in industry standards
- Identification of new threats
- Evaluation of adequacy of existing controls
- Benchmarking to comparable companies
How to create a privacy policy for different scenarios
- Essential clauses of a privacy policy
- Tone and drafting of a privacy policy
- How to draft clauses informing customers about their rights
- Appropriate methods of obtaining consent
- How to obtain consent in the event of amendment
- How to create a policy for a multi-jurisdictional organization
How to draft a cookie policy
How to create an acceptable use policy for data
Guidance materials:
- Work from home environment: Privacy guidelines issued by Information and Privacy Commissioner, Ontario
- Sample Privacy-related clauses for a work-from-home setting
- How to apply Privacy Impact Assessment Guidelines & Questionnaire under the Ontario Personal Health Information Protection Act in your organizational context
- How to apply Privacy impact Assessment Guidelines of the Philippines National Privacy Commission in your organizational context
How to implement a ‘privacy by design’ framework - 4 ECTS
“Privacy by design” implementation: examples to understand the context
- Online multiplayer game
- HR department using online skill testing service to shortlist candidates
- Threat mapping for each scenario
- Surveillance/ CCTVs in Mass Transit systems (includes cameras, loyalty cards, etc.)
- Facebook - Cambridge Analytica data scandal and litigation
- Biometrics Used in Casinos and Gaming Facilities;
- Smart Meters and the Smart Grid;
- Mobile Devices & Communications;
- Near Field Communications (NFC);
- RFIDs and Sensor Technologies;
- Redesigning IP Geolocation Data;
- Remote Home Health Care;
- Big Data and Data Analytics
7 Foundational Principles of Privacy by Design
- Proactive not Reactive; Preventative not Remedial
- Privacy as the Default Setting We can all be certain of one thing
- Privacy Embedded into Design
- Full Functionality — Positive-Sum, not Zero-Sum
- End-to-End Security — Full Lifecycle Protection
- Visibility and Transparency — Keep it Open
- Respect for User Privacy — Keep it User-Centric
- How to implement these in a real scenario
Methodology to implement Privacy by Design framework
- Implementation through Information Technology
- Implementation through Accountable Business Practices
- How to create such practices
- Implementation through Physical Design and Networked Infrastructure
Information security management for global organizations: Management system requirements under ISO 27001
- Opportunities for professionals in Information Security Management:
- Work in an organization which has implemented an information security management system
- Work as a consultant and assist organizations to comply
- Run internal or external audits
- Job roles
- Information security managers
- Information security consultants and auditors
- Information security officers
- Information security risk specialists
- People involved in the implementation and administration of information security management systems according to ISO/IEC 27001
- ISO 27000 family of standards
- How to create an information security policy
- Legal requirements in different jurisdictions for information security policy
- How to create an information security management system (ISMS)
- Phases of implementation: Context, Leadership, Planning, Support Operation, Performance Evaluation and Improvement
- Role of top management and organizational staff
- Information security policy for supplier relationships
- Responsibility for managing the functionality of the ISMS
- Monitoring, Measurement and Evaluation of ISMS
- Internal Audit of ISMS
- Reviews of information security
- Interrelationship of ISMS with legal and regulatory requirements
Template:
- Sample Information Security Policy
Key controls under ISO 27000
- Asset management under ISO 27000
- Mobile device policy for work from home and mobile scenarios
- Access Controls
- Cryptography
- Physical and environmental security
- Communications security
- System acquisition, development and maintenance
- Supplier relationships
- Information Security Incident Management under ISO
- Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity
- Operations security: Malware protection, backups, logging, technical vulnerability management, etc.
Thesis/Dissertation
12 ECTS
1. Thesis Outline
Candidates for the Master of Business Administration are requested to submit a thesis as concluding part-fulfilment for their Qualification. The thesis is focused on a topic being related to and essential for business and/or management.
2. Approved Topics
Generally, there is no limitation for the topic, it only needs to be specific regarding the learning objectives of this particular programme of studies. Essential is that the thesis provides significant evidence for a candidate’s capability to undertake own and independent research. Therefore, the research can take place in the context of, e.g.,
- an organisation and/or its functions
- the supply chain
- consumer- or customer-specific aspects
- economic considerations
- elements of sustainability, societal and/or environmental issues of business and/or management
- Further topics are allowed upon approval of the programme leader
Students can adopt an organisation or write a fully theory-based thesis, provided that both are related to empirical data and consequential conclusions (e.g., how theory, concepts or frameworks improve the value of organisational performance and/or management). Issues of and respect for sustainability, ethics and moral are important elements of any argumentation and discussion.
Within their thesis students are requested to provide evidence of their intellectual capability to undertake own and independent empirical research, which is robust, consistent and evidence-based. The thesis must meet the standards on postgraduate level.
3. Thesis Requirements and Specifications
- Submission of the thesis, which consists of 15,000 words (+/- 10%).
- Submission within 24 weeks after the start of the thesis module.
The thesis module counts as the core module, providing evidence for the overall learning achievements.
4. Admission to the Thesis
The thesis module can only be started, when all taught modules of the MBA program have been successfully completed.
Prior to start students will have to present a thesis proposal (cf. Research Methods module), in which they explain:
- The topic of their thesis related to business and/or management
- The relevance of the topic with regard to management principles
- The methodology including the strategy of research and method of data collection (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, mixed method research, case study, empirical study, etc.)
- The objectives of the intended research
5. Assessment of the Thesis
The assessment of the thesis is based on
- Relevance and appropriateness of the discussion and the research findings
- Academic depth and level of criticality
- Logic and relevance of the argumentation
- Robustness of the methodology
- Practice-orientation and theoretical consideration in the field of management
- Selection of academically acceptable literature, such as peer-reviewed and published research papers, book publications, relevant statistics and other academically acceptable publications
- Narrative style, presentation and structure of the thesis.
Official Transcript Format
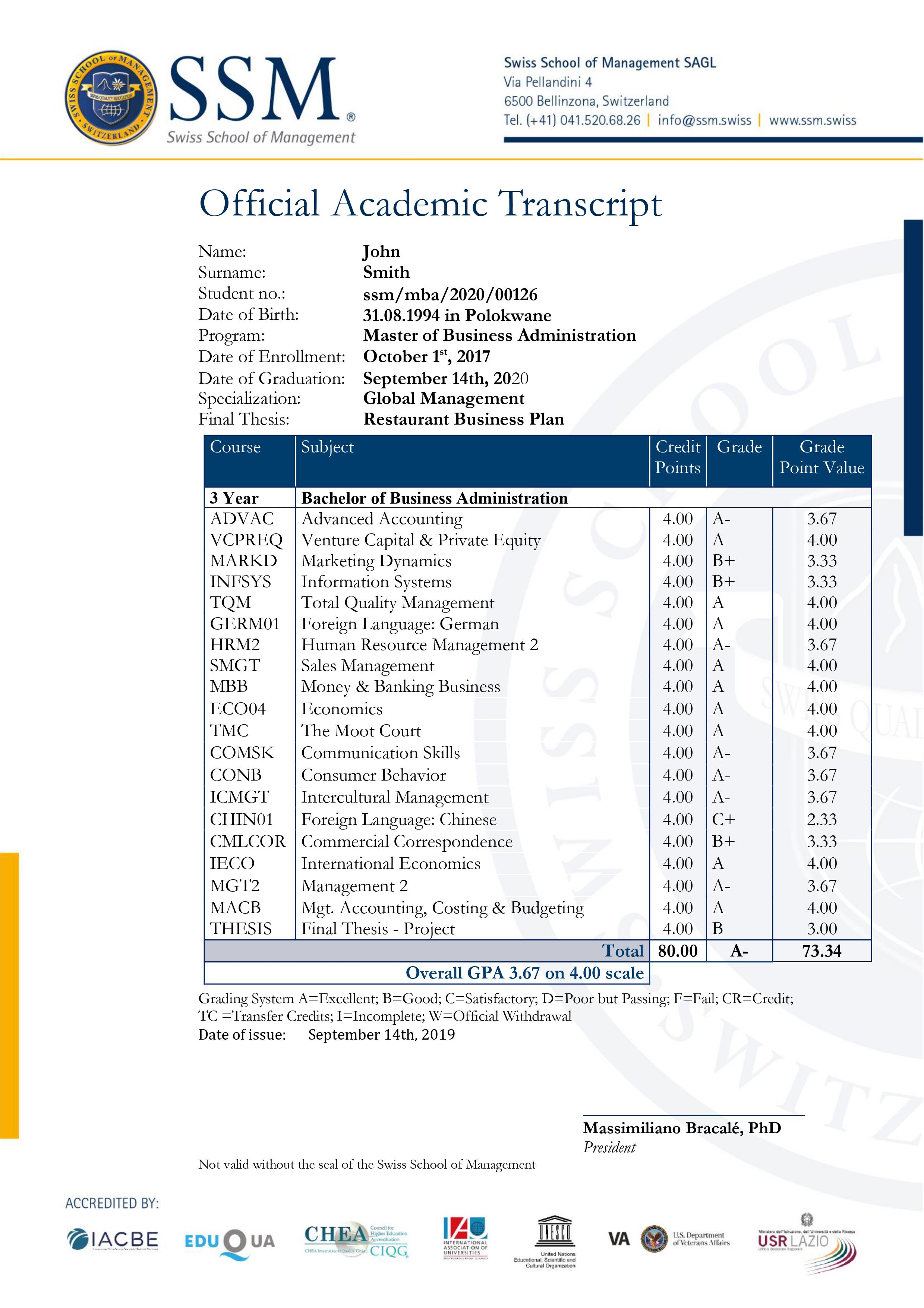
Syllabus
The Master of Business Administration program consists of 16 courses which comprise 12 core subject courses/modules, including a thesis and 10 specialization subjects.
It is mandatory to submit a final project/thesis or business plan in order to graduate.
The Master of Business Administration (MBA) university degree is granted to participants who achieve 90 ECTS (European Credit Transfer System)- this program has a total of 90 ECTS.
The minimum credit requirement for core subjects is 4 ECTS each.
25 learning hours correspond to 1 ECTS credit point. The total amount of learning is 100 hours for each module. Each module carries 4 ECTS credit points, some modules have been divided into 2 parts and thus carry 2 ECTS each.
Course Plan
Above prices are inclusive of all applicable taxes and charges.
 Standard
Standard
The degree awarded will be MBA in Data Protection and Privacy Management from Swiss School of Management.
It is a 15 months course that can be completed within 30 months to be eligible to receive the completion certificate (Degree).
The SSM MBA Degree is fully accredited by IACBE and CHEA-Council for Higher Education. SSM MBA degree is also accredited by the Department of Veterans Affairs in the USA. SSM is a quality certified school by EduQua, the Swiss Quality Certification label (accredited by the Swiss Federal Government) for Institutions of higher and continuous education







 Key Highlights
Key Highlights






 ADDICTIVE LEARNING TECHNOLOGY LIMITED
ADDICTIVE LEARNING TECHNOLOGY LIMITED











