UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 syllabus with unit-wise weightage analysis, 10-unit breakdown, previous year trends, and strategic preparation guide. Master all units and qualify with confidence.
Table of Contents
If you’re preparing for UGC NET Commerce, you’ve probably realised that Paper 2 is where the real battle lies. This is the paper that tests your subject expertise across 100 questions worth 200 marks, and your performance here largely determines whether you qualify for Assistant Professor or secure the coveted Junior Research Fellowship. Understanding not just the syllabus, but how questions are distributed across units, is what separates strategic candidates from those who prepare blindly.
The Commerce subject (Code 08) is one of the most popular choices among NET aspirants, which means competition is fierce. In December 2024, the JRF cut-off for General category stood at an average 210 marks out of 300, while Assistant Professor eligibility required 186 marks. These numbers tell you something important: you need a strong Paper 2 performance to clear these thresholds. That’s exactly why this guide exists.
In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll break down all 10 units of the Commerce Paper 2 syllabus, examine unit-wise weightage patterns based on previous year papers, and give you a strategic preparation framework. Whether you have six months or just three months before your exam, this guide will help you allocate your time wisely and focus on what actually gets asked. Let’s dive in.
UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
Paper 2 is the subject-specific component of the UGC NET examination that evaluates your in-depth knowledge of Commerce. Unlike Paper 1 which tests general teaching and research aptitude, Paper 2 focuses entirely on your understanding of commerce-related concepts ranging from accounting principles to taxation laws. This is where your postgraduate education comes into play, and the questions are designed to test whether you have the subject expertise required to teach at the university level.
The National Testing Agency (NTA) conducts this examination twice a year, typically in June and December sessions. Commerce consistently ranks among the top five subjects in terms of candidate registration, with lakhs of aspirants competing for limited JRF slots and Assistant Professor positions. This popularity means the competition is intense, and a superficial understanding of the syllabus simply won’t cut it.
Total Questions, Marks Distribution, and Time Allocation
Paper 2 consists of 100 multiple-choice questions, each carrying 2 marks, for a total of 200 marks. You get 2 hours to complete this paper, which means you have approximately 72 seconds per question. There is no negative marking, so you should attempt every single question even if you’re not completely sure about the answer. Leaving questions unattempted is essentially throwing away potential marks.
The time pressure is real, and this is where strategic preparation makes a difference. If you’ve practised enough previous year papers, you’ll recognise question patterns quickly and save precious seconds.
How Paper 2 Differs from Paper 1
Paper 1 is a common paper for all NET subjects and tests general aptitude across 10 units like teaching aptitude, research methodology, logical reasoning, and data interpretation. It carries 100 marks for 50 questions and takes 1 hour. The key difference is that Paper 1 questions are relatively straightforward and test general awareness, while Paper 2 requires deep conceptual understanding of your chosen subject.
Many candidates make the mistake of treating both papers with equal weightage, but consider this: Paper 2 is worth twice the marks (200 vs 100). Your subject-specific preparation directly impacts your Paper 2 score, and this is often the differentiator between JRF qualifiers and those who just clear the Assistant Professor threshold. A strong Paper 2 performance can compensate for an average Paper 1, but the reverse is rarely true.
Analysis of UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
When you analyse previous year papers systematically, patterns emerge that can significantly guide your preparation. The UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 covers 10 units, but not all units carry equal weightage in the actual examination. Some units consistently contribute 12-15 questions while others may have 6-8 or 7-9 questions. Understanding these patterns helps you prioritise your study time effectively.
Based on analysis of papers from 2020-2024, units like Accounting and Auditing, Business Finance, and Management consistently feature prominently. Meanwhile, units like Legal Aspects of Business and Banking often have fewer questions but are scoring for candidates who prepare them well. The key is to balance comprehensive coverage with strategic focus on high-weightage areas.
Unit-wise Weightage
The approximate unit-wise distribution based on previous year trends shows that Accounting and Auditing typically contributes 12-15 questions, making it the highest-weightage unit. Business Finance and Business Management each contribute around 10-12 questions. Marketing Management, Business Economics, and Taxation units typically have 8-10 questions each. The remaining units like Banking, Legal Aspects, and Business Environment usually contribute 6-8 questions each.
However, it’s important to note that NTA doesn’t follow a fixed pattern, and weightage can shift between sessions. What remains consistent is that numerically-oriented units like Accounting, Finance, and Statistics together constitute nearly 35-40% of the paper. Candidates strong in numerical concepts have a clear advantage, but theory-focused questions from Management and Marketing shouldn’t be underestimated either.
Syllabus for UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
The UGC NET Commerce syllabus is structured into 10 comprehensive units covering the entire spectrum of commerce education. Each unit represents a major domain within the discipline, and questions test both theoretical understanding and practical application. The syllabus is designed to evaluate whether you have the foundational knowledge required to teach postgraduate students in Indian universities.
Before we dive into each unit, remember that the official syllabus PDF is available on the NTA website in both Hindi and English. I strongly recommend downloading and printing this document to use as your preparation checklist. Mark topics as you complete them, and you’ll have a visual representation of your progress throughout your preparation journey.
Unit 1 – Business Environment and International Business
This unit forms the foundation for understanding how businesses operate within larger economic, political, and social contexts. It covers the conceptual framework of business environment including economic environment, political environment, legal environment, and socio-cultural factors. The international business component includes globalisation theories, modes of entry into international markets, and trade policies.
Questions from this unit often test your understanding of current economic policies, trade agreements, and international organisations. You’ll encounter topics like WTO regulations, regional trading blocs (SAARC, ASEAN, EU), foreign direct investment policies, and balance of payments concepts. The syllabus also includes corporate social responsibility and business ethics, which are increasingly relevant in today’s context.
Topics Covered: Globalisation, Trade Policies, and Business Ethics
Globalisation is a recurring theme with questions on its drivers, benefits, challenges, and impact on Indian businesses. You should understand different theories of international trade including absolute advantage, comparative advantage, and the Heckscher-Ohlin model. Trade policies cover both tariff and non-tariff barriers, and questions often test your knowledge of India’s foreign trade policy provisions.
Business ethics and CSR have gained prominence in recent papers. Questions may ask about ethical frameworks, corporate governance principles, and India’s CSR regulations under the Companies Act 2013. Environmental concerns and sustainable business practices are also covered under this unit, reflecting the growing importance of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) considerations in modern commerce.
Estimated Weightage and Question Patterns
This unit typically contributes 6-8 questions in Paper 2. Questions are predominantly theoretical and conceptual, testing your understanding of frameworks rather than numerical calculations. You’ll find direct questions on definitions, matching questions linking concepts with their proponents, and application-based questions presenting business scenarios.
A common pattern is questions on international trade theories asking you to identify which theory explains a particular trade phenomenon. Questions on business environments often present case scenarios where you need to identify the environmental factor (economic, political, legal, or social) affecting a business decision. Preparing crisp notes on key theories and their proponents will help you answer these quickly.
Unit 2 – Accounting and Auditing
This is arguably the most important unit in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2, consistently contributing the highest number of questions. It covers financial accounting, cost accounting, management accounting, and auditing standards. You’ll need strong conceptual clarity on accounting standards (both Indian AS and IFRS), preparation of financial statements, and various costing methods.
The auditing portion covers types of audits, audit planning and procedures, vouching, verification of assets and liabilities, and audit reporting. Recent trends in auditing including forensic auditing, environmental auditing, and IT auditing are also part of the syllabus. Given the weightage, this unit deserves significant preparation time regardless of your comfort level with accounting.
Core Concepts You Must Master
For financial accounting, focus on partnership accounts, company accounts, holding company accounts, and accounting for amalgamation. Cost accounting concepts like marginal costing, standard costing, budgetary control, and cost-volume-profit analysis are frequently tested. Management accounting topics include ratio analysis, fund flow analysis, cash flow analysis, and responsibility accounting.
Auditing concepts require understanding of internal control systems, audit evidence, audit sampling, and auditor’s liability. You should know the differences between internal audit and statutory audit, and understand the provisions related to company audit under the Companies Act 2013. The recent amendments to auditing standards and their implications are also important.
Numerical vs Theoretical Question Split
In this unit, expect roughly a 40-60 split between numerical and theoretical questions. Numerical questions typically involve simple calculations like ratio computation, cost determination, or profit calculation. They’re not complex but require accuracy and quick mental math. The theoretical questions test your understanding of accounting standards, auditing procedures, and conceptual frameworks.
A smart strategy is to attempt numerical questions first as they offer definitive answers with less ambiguity. If you know the formula and can calculate accurately, you’ll definitely score. Theoretical questions sometimes have closely worded options that can confuse you under time pressure. Practising previous year numericals is the best preparation for this unit.
Unit 3 – Business Economics
Business Economics bridges microeconomic and macroeconomic concepts with business decision-making. This unit covers demand and supply analysis, production and cost theory, market structures, pricing strategies, and national income concepts. The focus is on how economic principles apply to business situations rather than pure economic theory.
You’ll encounter topics like elasticity of demand, consumer behaviour theories, production functions, cost concepts (short-run and long-run), and equilibrium analysis under different market conditions. Macroeconomic concepts include business cycles, inflation, monetary and fiscal policy, and their impact on business decisions.
Important Economic Theories and Concepts
Microeconomic theories form the bulk of questions from this unit. You should thoroughly understand consumer equilibrium under cardinal and ordinal approaches, producer equilibrium, and price-output determination under perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. Indifference curve analysis and production possibility frontier concepts are frequently tested.
Macroeconomic topics include Keynesian economics, multiplier effect, IS-LM model basics, and determination of national income. Questions often test your understanding of fiscal and monetary policy tools and their economic effects. Recent papers have also included questions on contemporary economic issues relevant to India’s economic environment.
Question Framing Patterns in Economics
Economics questions in NET Commerce follow predictable patterns. You’ll find graphical analysis questions where you need to interpret shifts in demand-supply curves or identify equilibrium positions. Conceptual questions test definitions and characteristics of economic phenomena. Application questions present scenarios where you apply economic principles to business decisions.
Numerical questions in this unit typically involve elasticity calculations, cost-output computations, or simple national income problems. These are scoring if you’re comfortable with basic economics formulas. The theoretical questions often use diagrams, so being able to visualise and interpret economic graphs is an advantage during the exam.
Unit 4 – Business Finance
Business Finance is another high-weightage unit focusing on financial management concepts. It covers the time value of money, capital budgeting decisions, capital structure theories, cost of capital, dividend policy, and working capital management. This unit has significant numerical components and rewards candidates with strong financial management fundamentals.
The syllabus includes contemporary topics like financial derivatives, risk management, and portfolio theory. Questions test your understanding of how firms make financing decisions, investment decisions, and dividend decisions. Theoretical concepts like MM hypothesis, trade-off theory, and pecking order theory are important for this unit.
Financial Management Topics to Focus On
Capital budgeting is a favourite area for examiners. You should master techniques like NPV, IRR, Payback Period, and Profitability Index. Understanding the assumptions, advantages, and limitations of each technique is equally important for theoretical questions. Capital structure theories including net income approach, net operating income approach, and MM propositions (with and without taxes) are frequently tested.
Working capital management covers cash management models (Baumol and Miller-Orr), receivables management, and inventory management techniques. Dividend policy theories including Walter model, Gordon model, and MM dividend irrelevance hypothesis require conceptual clarity. Cost of capital calculations for different sources (debt, equity, retained earnings) and WACC computation are essential.
Calculation-Based Questions
Expect 5-7 numerical questions from Business Finance alone. These typically involve capital budgeting calculations (NPV, IRR), cost of capital computations, or leverage analysis. The calculations aren’t complex, but they require familiarity with formulas and careful attention to the data provided in questions. Time value of money concepts underpin many calculations.
A common mistake is spending too much time on complex numericals. If a calculation seems too lengthy for the 72-second average time, mark it for review and move on. Often, Finance numericals can be simplified using shortcuts or elimination techniques. Practice is the key, and solving previous year numerical questions will build both speed and confidence.
Unit 5 – Business Statistics and Research Methods
This unit combines quantitative techniques with research methodology. The statistics portion covers measures of central tendency, dispersion, correlation, regression, probability distributions, and hypothesis testing. Research methodology includes research design, sampling techniques, data collection methods, and report writing.
Many Commerce graduates find statistics challenging, but the questions in NET are not overly complex. The focus is on understanding when to apply which technique rather than extensive calculations. Research methodology questions test your understanding of the research process and appropriate methodological choices for different research situations.
Statistical Tools and Research Methodology Coverage
For statistics, focus on descriptive statistics (mean, median, mode, standard deviation, coefficient of variation), correlation and regression analysis, and index numbers. Probability concepts including theoretical and empirical probability, probability distributions (binomial, Poisson, normal), and sampling distributions are part of the syllabus.
Research methodology covers the entire research process from problem formulation to report writing. You should understand different research designs (exploratory, descriptive, causal), sampling methods (probability and non-probability), data collection instruments, and reliability and validity concepts. Hypothesis testing including types of errors (Type I and Type II) is important.
Probability and Hypothesis Testing Essentials
Probability questions typically test basic probability rules, conditional probability, and Bayes theorem. Distribution-related questions may ask you to identify the appropriate distribution for a given situation or calculate probabilities using standard formulas. These are scoring if you understand the concepts clearly.
Hypothesis testing questions focus on conceptual understanding rather than complex calculations. You should know the steps in hypothesis testing, understand p-value interpretation, and differentiate between one-tailed and two-tailed tests. Questions on ANOVA, chi-square test, and non-parametric tests may appear, testing your knowledge of when each test is appropriate.
Unit 6 – Business Management and Human Resource Management
This comprehensive unit covers management principles, functions, and theories along with the entire spectrum of human resource management. Management topics include planning, organising, leading, and controlling functions. Contemporary management concepts like strategic management, change management, and knowledge management are included.
HRM covers human resource planning, recruitment and selection, training and development, performance appraisal, compensation management, and employee welfare. Industrial relations, trade unions, and labour legislation also fall under this unit. Given the breadth of coverage, this unit requires systematic preparation across multiple sub-areas.
Management Theories and HR Concepts
Classical management theories (Taylor, Fayol, Weber), neo-classical theories (Hawthorne studies, human relations approach), and modern management theories (systems approach, contingency theory) are frequently tested. You should know the contributions of major management thinkers and be able to match theories with their proponents.
For HRM, understand the strategic role of HR in organisations, competency mapping, and HR analytics. Recruitment and selection processes, training methods, performance appraisal techniques (MBO, 360-degree feedback, BARS), and compensation structures are important topics. Industrial relations concepts including collective bargaining, workers’ participation, and dispute resolution mechanisms are also covered.
Application-Based Question Approach
This unit features many application-based questions presenting organisational scenarios. You’ll need to identify which management principle or HR technique applies to the given situation. Questions may ask you to recommend solutions for organisational problems or evaluate the suitability of different management approaches.
Unit 7 – Banking and Financial Institutions
This unit covers the Indian banking system, Reserve Bank of India functions, monetary policy, and various financial institutions. Topics include commercial banking, development banking, cooperative banking, and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs). Recent developments in banking including digital banking, financial inclusion, and Basel norms are also covered.
Understanding RBI’s monetary policy tools and their economic effects is crucial for this unit. The syllabus includes financial markets (money market and capital market), financial instruments, and regulatory frameworks. Questions often test your knowledge of current banking sector developments and policy changes.
RBI, Monetary Policy, and Banking Structure
The Reserve Bank of India’s functions as a central bank form the core of this unit. You should understand RBI’s role as banker to the government, banker’s bank, and regulator of the banking sector. Monetary policy tools including repo rate, reverse repo rate, CRR, SLR, and open market operations are frequently tested.
The structure of Indian banking including scheduled and non-scheduled banks, public and private sector banks, and the role of development banks like NABARD, SIDBI, and EXIM Bank is important. Recent banking sector reforms, consolidation through mergers, and the evolution of payment systems are contemporary topics that appear in questions.
Current Affairs Integration in Banking Questions
Banking questions often integrate current developments with conceptual knowledge. Recent topics include digital currency initiatives, UPI adoption, financial inclusion measures (Jan Dhan Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana), and regulatory changes affecting NBFCs. Questions may test your awareness of recent RBI circulars and their implications.
Basel norms and capital adequacy requirements for banks are technical topics that require conceptual clarity. Understanding the evolution from Basel I to Basel III and India’s implementation timeline helps answer questions on banking regulation. Priority sector lending norms and NPA management frameworks are also important contemporary topics.
Unit 8 – Marketing Management
Marketing Management covers the complete marketing function from understanding consumer needs to delivering value through products and services. Topics include marketing concepts and philosophies, marketing mix (4Ps extended to 7Ps for services), market segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP), and consumer behaviour theories.
Contemporary marketing topics like digital marketing, social media marketing, green marketing, and relationship marketing are increasingly important. The syllabus also covers marketing research, product life cycle management, branding strategies, and distribution channel management. This unit rewards candidates who understand practical marketing applications.
Marketing, Consumer Behaviour, and Digital Marketing
Consumer behaviour is a significant portion of this unit. You should understand the consumer decision-making process, factors influencing consumer behaviour (cultural, social, personal, psychological), and models of consumer behaviour (Howard-Sheth, Nicosia, Engel-Kollat-Blackwell). Organisational buying behaviour differs from consumer buying and is also covered.
Digital marketing has gained prominence in recent papers. Topics include search engine optimization, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, and marketing analytics. Understanding how digital channels integrate with traditional marketing for integrated marketing communication is important for contemporary questions.
Case Study Style Questions in Marketing
Marketing questions often present case scenarios requiring you to apply marketing concepts. You may need to identify appropriate segmentation variables, recommend positioning strategies, or evaluate marketing mix decisions. These questions test your ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical business situations.
Product life cycle questions are common, asking you to identify the stage and recommend appropriate marketing strategies. Pricing strategy questions may present scenarios requiring you to identify which pricing approach (penetration, skimming, competitive, value-based) is most suitable. Brand management questions test concepts like brand equity, brand extension, and co-branding.
Unit 9 – Legal Aspects of Business
This unit covers various laws affecting business operations in India. Major legislation includes the Indian Contract Act 1872, Sale of Goods Act 1930, Companies Act 2013, Consumer Protection Act 2019, Competition Act 2002, and Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) laws. Understanding the provisions of these acts and their business implications is essential.
The syllabus also includes information technology law (IT Act 2000), environmental legislation, and labour laws. Given that many Commerce students don’t have a legal background, this unit requires dedicated preparation. However, questions typically test basic provisions and general understanding rather than detailed legal interpretation.
Key Acts and Legal Provisions to Study
The Indian Contract Act is foundational, covering essential elements of a valid contract, types of contracts, performance and discharge of contracts, breach and remedies, and special contracts (indemnity, guarantee, bailment, agency). Sale of Goods Act provisions on conditions and warranties, transfer of property, and rights of unpaid sellers are important.
Companies Act 2013 is extensive, but focuses on company formation, types of companies, prospectus provisions, share capital, company management (directors, meetings), and winding up provisions. Consumer Protection Act 2019 provisions on consumer rights, consumer disputes, redressal machinery, and product liability are frequently tested.
How Law Questions Appear in Commerce Paper
Legal questions in Commerce Paper 2 are relatively straightforward compared to law-specific exams. You’ll encounter questions asking about provisions of specific sections, case scenario-based questions testing application of legal principles, and matching questions linking legal concepts with their definitions.
IPR questions cover patents, copyrights, trademarks, and geographical indications at a basic level. You should understand the registration process, protection period, and infringement remedies for each type of intellectual property. Competition Act provisions on anti-competitive agreements, abuse of dominant position, and combinations are also covered.
Unit 10 – Income Tax and Corporate Tax Planning
This unit covers direct taxation with focus on income tax provisions and corporate tax planning strategies. Topics include basic concepts of income tax (previous year, assessment year, residential status, incidence of tax), computation of income under different heads, deductions, and tax liability calculation.
Corporate tax planning covers legitimate methods for tax minimisation, tax planning versus tax evasion versus tax avoidance, and specific tax planning strategies for business decisions. Recent amendments in tax laws and their implications for businesses are part of the syllabus, making this a dynamic unit requiring current knowledge.
Taxation Concepts and Computation Topics
Understanding the five heads of income (salary, house property, business/profession, capital gains, other sources) and computation under each head is fundamental. Deductions under Chapter VI-A, set-off and carry forward of losses, and tax rates for different categories of assessees (individuals, companies) are important concepts.
For corporate taxation, focus on MAT (Minimum Alternative Tax) provisions, dividend distribution tax changes, and presumptive taxation schemes. Tax planning for specific business decisions like make vs buy, own vs lease, and business expansion requires understanding the tax implications of different options.
Recent Amendments and Their Exam Relevance
Taxation is a dynamic area with annual amendments through Finance Acts. Recent changes like new tax regime options for individuals, corporate tax rate reductions, and faceless assessment procedures have examination relevance. You should be aware of major amendments from the last 2-3 Finance Acts.
Questions on taxation may test computational ability (simple income tax calculations) or conceptual understanding (identifying tax planning opportunities, classifying income under correct heads). Given the technical nature, maintaining updated knowledge through official sources like the Income Tax Department website is advisable.
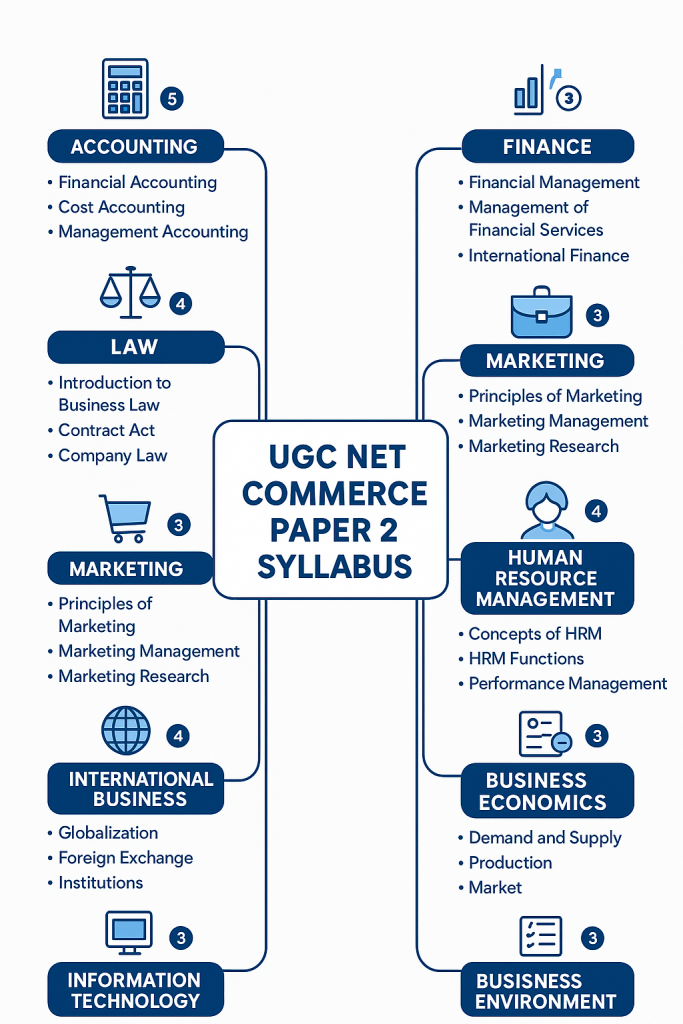
UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 Weightage Analysis: 5-Years Trend
Understanding how questions are distributed across units is perhaps the most strategic insight you can gain for Paper 2 preparation. While NTA doesn’t officially publish unit-wise weightage, careful analysis of previous year papers reveals consistent patterns that can guide your preparation priorities. Let’s examine what the data from 2020-2024 papers tells us.
The UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 has shown relatively stable question distribution over the years, with some units consistently dominating while others show fluctuating importance. This stability is actually advantageous for preparation, as you can reasonably predict which areas deserve more of your study time. However, the caveat is that NTA can introduce surprises, so complete syllabus coverage remains important.
Units with maximum weightage in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
Units with Consistently High Question Count
Accounting and Auditing has emerged as the undisputed leader in question contribution, typically accounting for 12-15 questions (24-30 marks) in each paper. This single unit can contribute up to 15% of your Paper 2 score. Business Finance follows closely with 10-12 questions, making these two numerically-oriented units together worth approximately 25% of the paper.
Business Management and HRM, despite being a broad unit, consistently contributes 10-12 questions. Combined with Marketing Management (8-10 questions), the management-related units constitute another significant portion of the paper. This means candidates with strong fundamentals in accounting, finance, and management have a natural advantage in scoring well.
Emerging Topics Gaining Weightage
Recent papers show increased emphasis on contemporary topics within each unit. Digital marketing questions have increased within the Marketing unit. E-commerce, fintech, and digital banking questions are appearing more frequently in the Banking unit. Research methodology, particularly data analysis techniques and research ethics, is gaining importance within the Statistics unit.
How to Prepare for UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
Now that you understand the syllabus and weightage patterns, let’s translate this knowledge into an actionable preparation strategy. The key to cracking UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 is not just studying hard but studying smart, focusing your energy on high-return areas while maintaining comprehensive coverage. Your preparation approach should be structured, time-bound, and regularly evaluated through mock tests.
Whether you have six months or three months before your exam, the principles remain the same: prioritise high-weightage units, master fundamentals before moving to advanced topics, and practice extensively with previous year papers. The difference lies in depth of coverage and revision cycles, but even time-constrained candidates can qualify with strategic preparation.
Unit-Wise Study Plan for UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
Time Allocation for Each Unit (Recommended Schedule)
Based on weightage analysis, focus your strongest preparation efforts on Accounting and Auditing; this should be your primary area of concentration. Business Finance deserves substantial attention given its numerical emphasis and scoring potential. Business Management and HRM combined warrant significant time investment, while Marketing Management needs consistent but moderate preparation. These four areas should form the core of your study plan.
The remaining units require steady attention without dominating your schedule. Business Economics and Statistics need regular practice to maintain proficiency. Legal Aspects and Taxation each deserve focused sessions to master their key concepts, while Business Environment and Banking can be covered through shorter, targeted study periods. This approach ensures comprehensive coverage while prioritising high-scoring areas.
Best Sequence to Study UGC NET Commerce Units
Start with Accounting and Auditing as it’s foundational and carries maximum weightage. Early mastery of this unit builds confidence and ensures your strongest area is well-prepared. Follow with Business Finance, as many concepts overlap with accounting and the unit rewards early practice. These two units together form your scoring core.
Move to Business Management and HRM next, followed by Marketing Management, as these units are relatively easier to cover and provide mental relief from numerical subjects. Then tackle Business Economics and Statistics. Save Legal Aspects, Taxation, Business Environment, and Banking for the final phase, as these units benefit from current affairs integration and recent revision.
Best Books and Resources for Commerce Paper 2
Textbooks for Conceptual Clarity
Selecting the right books is crucial for mastering the UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 syllabus, which spans across 10 units. For foundational units like Business Environment (Unit 1), the International Business Environment by Sundaram K. Anant & Black Stewart offers case-based insights into globalization and trade policies. Unit 2’s Accounting and Auditing is well-covered by Fundamentals of Accounting & Auditing by Ruchi Gupta, providing clear explanations of financial statements and auditing standards. Similarly, Unit 3’s Business Economics benefits from Business Economics by H.L. Ahuja for microeconomic principles.
For mid-syllabus units, Unit 4’s Business Finance draws from Business Finance by S.P. Gupta, emphasising capital budgeting techniques. Unit 5’s Statistics and Research Methods is strengthened by Business Statistics & Operation Research by Dr. S.P. Gupta et al., with practical exercises on regression and hypothesis testing. Unit 6’s Management and HRM shines through Fundamentals of Human Resource Management by Raymond A. Noe et al., detailing appraisal methods and organizational theories.
Rounding out the preparation, Unit 7’s Banking uses Banking Awareness by Arihant Experts for current RBI tools, while Unit 8’s Marketing relies on Marketing Management by Philip Kotler et al. for STP strategies. Units 9 and 10, Legal Aspects and Taxation, are supported by Legal Aspects of Business by P.K. Padhi and Corporate Tax Planning & Management by Dr. H.P. Mehrotra & Dr. S.P. Goyal. Comprehensive guides like Arihant’s NTA UGC NET/JRF/SET Paper 2 Commerce integrate all units with PYQs for holistic revision.
PYQ Books and Mock Test Resources
Previous year question papers are your most important preparation resource. IFAS Publications offers compiled PYQs from 2014-2025 with detailed explanations sorted unit-wise. The NTA website provides official previous papers and answer keys that you should definitely access. Solving at least 5 years of papers thoroughly is essential.
Conclusion
UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 is challenging but entirely conquerable with strategic preparation. The key insights from this analysis are clear: Accounting and Auditing, Business Finance, and Management together constitute nearly 50% of your paper, so these units deserve proportionally higher attention. Numerical concepts from accounting, finance, and statistics are scoring because they offer definitive answers without ambiguity.
Your preparation should follow a structured approach, starting with high-weightage units and building toward comprehensive coverage. Use standard textbooks for conceptual clarity, but don’t forget that previous year papers are your best predictors of what to expect. Mock tests are essential in the final phase to build speed and accuracy under exam conditions. With consistent effort and smart strategy, qualifying UGC NET Commerce is well within your reach. For more guidance on UGC NET preparation, explore LawSikho’s comprehensive resources that have helped hundreds of candidates achieve their academic career goals.
Frequently Asked Questions on UGC NET Commerce Paper 2
What is the weightage of each unit in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
Based on previous year paper analysis, Accounting and Auditing typically contributes 12-15 questions (12-15%), Business Finance 10-12 questions (10-12%), and Management/HRM 10-12 questions (10-12%). Marketing, Economics, Statistics, and Taxation each contribute approximately 8-10 questions. Legal Aspects, Banking, and Business Environment usually have 6-8 questions each.
Which units are most important for UGC NET Commerce?
Accounting and Auditing is the most important unit based on consistent high weightage across papers. Business Finance ranks second due to its scoring nature and numerical components. Business Management and HRM is third given its broad coverage and reliable question count. Focusing on these three units thoroughly can secure approximately 35-40% of your Paper 2 score.
How many questions come from Accounting and Auditing in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
Accounting and Auditing typically contributes 12-15 questions in Commerce Paper 2, making it worth 24-30 marks. This includes questions on financial accounting, cost accounting, management accounting, and auditing. The split between accounting and auditing questions is approximately 60-40, with more emphasis on accounting concepts.
Is there negative marking in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
No, there is absolutely no negative marking in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 or Paper 1. Each correct answer earns you 2 marks, and incorrect or unattempted questions carry zero marks. This means you should attempt every single question, even if you need to make an educated guess, as there’s no penalty for wrong answers.
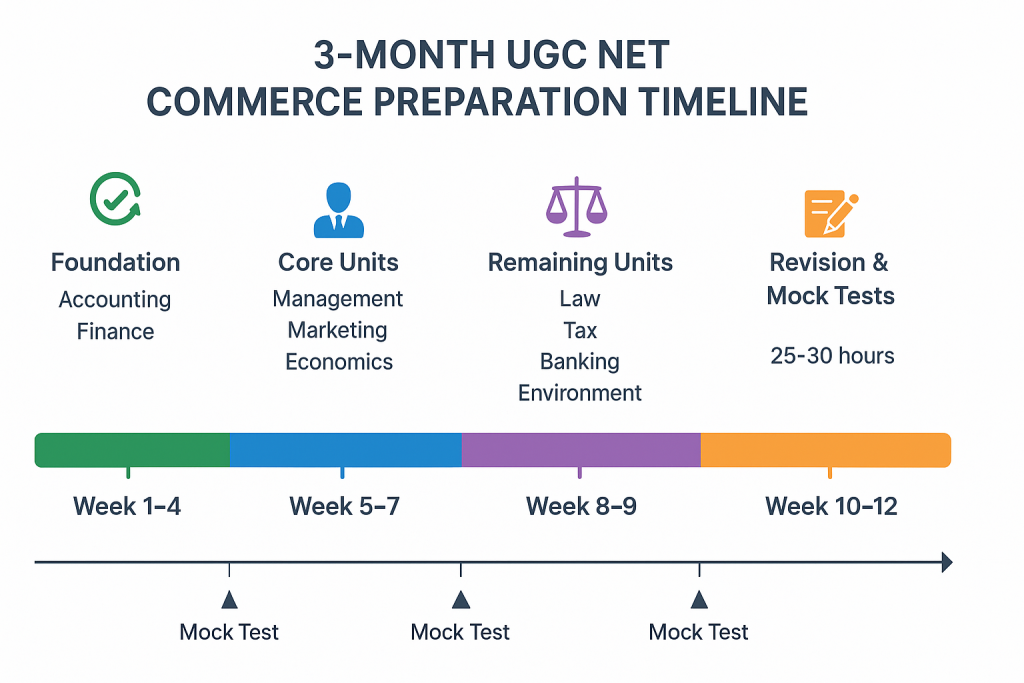
How to prepare for UGC NET Commerce Paper 2 in 3 months?
Dedicate the first month exclusively to Accounting, Auditing, and Business Finance with 3-4 hours daily study. Spend weeks 5-7 on Management, Marketing, and Economics. Cover remaining units (Law, Tax, Banking, Environment, Statistics) in weeks 8-9. Reserve the final 3 weeks for revision and mock tests. Solve at least 5 previous year papers completely during this period.
What is the difficulty level of UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
Commerce Paper 2 is considered moderate to challenging. Approximately 40% questions are direct or conceptual, 30% are application-based requiring analysis, and 30% are of moderate difficulty involving numerical calculations or matching concepts. The June 2025 paper was rated moderate by most candidates, with 60-70 good attempts being reported as average.
How many questions should I attempt to qualify UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
You should attempt all 100 questions since there’s no negative marking. For qualification as Assistant Professor (General category), you need at least 40% aggregate in Paper 1 and Paper 2.
Are numerical questions important in UGC NET Commerce?
Yes, numerical questions are highly important and scoring. Approximately 25-30 questions across the paper involve calculations from Accounting, Finance, Statistics, Economics, and Taxation units. These questions offer definitive answers with no ambiguity, making them easier to score compared to theory questions with closely-worded options.
What is the cut-off for UGC NET Commerce JRF?
For December 2024, the JRF cut-off for General category in Commerce was 210 marks out of 300 (70%). For Assistant Professor, it was 186 marks (62%), and for PhD only, it was 162 marks (54%). OBC, SC, ST, EWS, and PwD categories have progressively lower cut-offs as per reservation policy. These figures vary each session based on exam difficulty and candidate performance.
How to cover the vast syllabus of UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
Prioritise units by weightage rather than studying sequentially. Create summary notes for each unit as you study, which will accelerate revision. Focus on concepts rather than memorising facts, as NET tests understanding. Use previous year papers to identify frequently asked topics within each unit. Study 3-4 hours daily with weekly revision of completed units.
Which topics are repeated frequently in UGC NET Commerce Paper 2?
Frequently repeated topics include ratio analysis, cost-volume-profit analysis, and capital budgeting from Accounting/Finance units. Management theories (Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor) and marketing mix concepts appear regularly. Consumer behaviour models, RBI functions, and Companies Act provisions are recurring themes. Income computation under different heads and contract essentials from legal aspects are also repeated frequently.




 Allow notifications
Allow notifications