Master the UGC NET syllabus with our complete Paper 1 and Paper 2 breakdown. Get unit wise topics, weightage analysis and preparation strategies.
Table of Contents
So you’re eyeing that Assistant Professor position or dreaming of a Junior Research Fellowship? Here’s the deal: cracking UGC NET starts with one non negotiable step: mastering the syllabus inside out.
Here’s what most aspirants get wrong: they dive into random preparation without understanding what they’re actually up against. The result? Wasted months and missed opportunities. But you’re not going to make that mistake.
This isn’t your typical syllabus breakdown. We’re giving you the complete UGC NET roadmap, Paper I’s ten units, Paper II’s subject specific deep dive across 85 disciplines, plus the strategic insights on weightage and priorities that coaching centers charge thousands for. Whether you’re aiming for Law, Commerce, English, or any other subject, we’ve got you covered.
Ready to turn that UGC NET dream into reality? Let’s break down exactly what stands between you and qualification.
UGC NET Exam Structure and Pattern
Before diving into syllabus specifics, you need a crystal clear understanding of how the examination is structured. The UGC NET exam consists of two papers conducted in a single three hour session without any break between them.
Both papers are computer based tests (CBT) featuring objective type multiple choice questions. Understanding this structure helps you plan your time management strategy during preparation and on exam day.
Marking Scheme and Question Distribution
The marking scheme for UGC NET is straightforward and candidate friendly. Each correct answer earns you 2 marks, and there is absolutely no negative marking for incorrect responses.
This means you should attempt every single question without fear of losing marks. The total examination carries 300 marks, distributed between the two papers based on their question counts and complexity levels.
Paper I: 50 Questions for 100 Marks
Paper I comprises 50 multiple choice questions worth 100 marks total. This paper assesses your teaching and research aptitude through ten distinct units covering areas like logical reasoning, data interpretation, communication skills, and awareness of higher education systems. According to the NTA official guidelines, five questions are typically set from each unit, meaning you cannot afford to neglect any section if you want maximum scores.
Paper II: 100 Questions for 200 Marks
Paper II consists of 100 questions carrying 200 marks, focusing entirely on your chosen subject. Whether you’ve selected Law, Commerce, English, Political Science, or any of the 85 subjects available, this paper tests your in depth knowledge and analytical abilities in that specific domain. The questions range from factual recall to application based problems, requiring thorough preparation across the entire subject syllabus.
Paper I vs Paper II: Key Differences
The fundamental difference lies in their purpose and scope. Paper I assesses your general aptitude for teaching and research careers, evaluating skills that every educator needs, regardless of their specialization. Paper II, conversely, examines your mastery of subject specific content that you’ll teach or research.
Many candidates make the mistake of focusing heavily on Paper II while underestimating Paper I, which can cost them their qualification since minimum qualifying marks are required in both papers separately.
Has the UGC NET Syllabus Changed in 2025 and for the Year 2026?
Here’s some good news for your preparation planning: the UGC NET syllabus has remained largely stable since the last major revision in 2019. The University Grants Commission typically revises the syllabus every 5 to 8 years, meaning the current syllabus framework will likely continue for the December 2025 session and into 2026.
However, you should always verify the official syllabus on the NTA website before finalizing your study plan, as minor topic additions or emphasis changes can occur through official notifications.
UGC NET Paper I Syllabus
Paper I is your gateway to demonstrating teaching and research aptitude. This common paper tests every UGC NET aspirant on ten comprehensive units designed to evaluate analytical thinking, comprehension abilities, communication proficiency, and awareness of academic systems.
Let’s break down each unit so you know exactly what to study.
Unit 1: Teaching Aptitude
Teaching Aptitude forms the foundation of Paper I. This unit evaluates your understanding of the teaching learning process, learner characteristics, and modern pedagogical approaches that every aspiring professor must master.
Teaching Methods, Learner Characteristics and Evaluation Systems
This unit covers the concept, objectives, and levels of teaching, including memory, understanding, and reflective levels. You need to understand learner characteristics for both adolescent and adult learners across academic, social, emotional, and cognitive dimensions.
The syllabus also includes factors affecting teaching related to teachers, learners, support materials, instructional facilities, learning environment, and institutions.
Methods of teaching in higher learning institutions, comparing teacher centered versus learner centered approaches, along with offline versus online methods like SWAYAM, SWAYAMPRABHA, and MOOCs are essential topics.
Teaching Aptitude Important Topics
Based on previous year analysis, Teaching Aptitude questions focus heavily on evaluation systems, including elements and types of evaluation, Choice Based Credit System (CBCS), and innovations in assessment methods.
The teaching support systems covering traditional, modern, and ICT based approaches are frequently tested. Questions often require you to distinguish between different teaching methodologies and identify appropriate approaches for specific learning scenarios.
You should pay special attention to the characteristics of effective teaching and the basic requirements for successful classroom instruction.
Understanding the relationship between teaching objectives and learning outcomes is crucial, as application based questions often test this connection. Many candidates score well by mastering the comparison between formative and summative evaluation methods.
Unit 2: Research Aptitude Syllabus for UGC NET
Research Aptitude is arguably the most important unit for JRF aspirants and carries significant weightage. This unit tests your understanding of research methodology, ethics, and the application of ICT in academic research.
Research Methods: Qualitative, Quantitative and Experimental
The syllabus covers the meaning, types, and characteristics of research along with positivism and post positivistic approaches.
You must understand experimental, descriptive, historical, qualitative, and quantitative research methods thoroughly.
The steps of research from problem identification through hypothesis formulation to data analysis and conclusion form core content. Thesis and article writing including format and styles of referencing such as APA, MLA, and Chicago are tested regularly.
Research Ethics and ICT in Research
Research ethics has gained increased importance in recent examinations.
You need to understand ethical principles governing academic research including plagiarism, data fabrication, and authorship issues.
The application of ICT in research covering digital libraries, online databases, reference management software, and research collaboration tools represents modern additions to the syllabus that align with contemporary academic practices.
Unit 3: Comprehension Syllabus for UGC NET
Comprehension is a passage based unit that tests your reading and analytical abilities. Unlike other units where you can prepare specific content, this section requires skill development through regular practice.
Comprehension Passage Format and Question Types
This unit presents a passage followed by questions testing your interpretation, inference, and analytical reasoning abilities.
The passages may be drawn from academic, scientific, or general interest topics.
Questions typically ask you to identify main ideas, draw conclusions, understand vocabulary in context, and analyze the author’s purpose or tone.
Regular practice with diverse reading materials improves your speed and accuracy in this section, which can be a scoring opportunity if approached strategically.
Unit 4: Communication Syllabus for UGC NET
Communication skills are essential for every educator, and this unit tests your understanding of how effective communication happens in academic and professional settings.
Verbal and Non Verbal Communication in UGC NET
The syllabus covers the meaning, types, and characteristics of communication along with effective communication strategies including verbal and non verbal elements.
You must understand inter cultural and group communications as well as classroom communication dynamics.
Barriers to effective communication and strategies to overcome them are frequently tested. The unit also covers mass media and society, exploring how media influences educational and social communication patterns.
Unit 5: Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude Syllabus
This unit tests your numerical and mathematical reasoning abilities through various problem types that you might find in competitive examinations.
Number Series, Percentage, Profit and Loss and Time and Distance
The syllabus includes types of reasoning, number series, letter series, codes, and relationships.
Mathematical aptitude topics cover fractions, time and distance, ratio and proportion, percentages, profit and loss, simple and compound interest, discounting, and averages.
While this unit might seem challenging for non mathematics backgrounds, consistent practice with previous year questions helps identify common patterns and shortcuts that make these problems manageable.
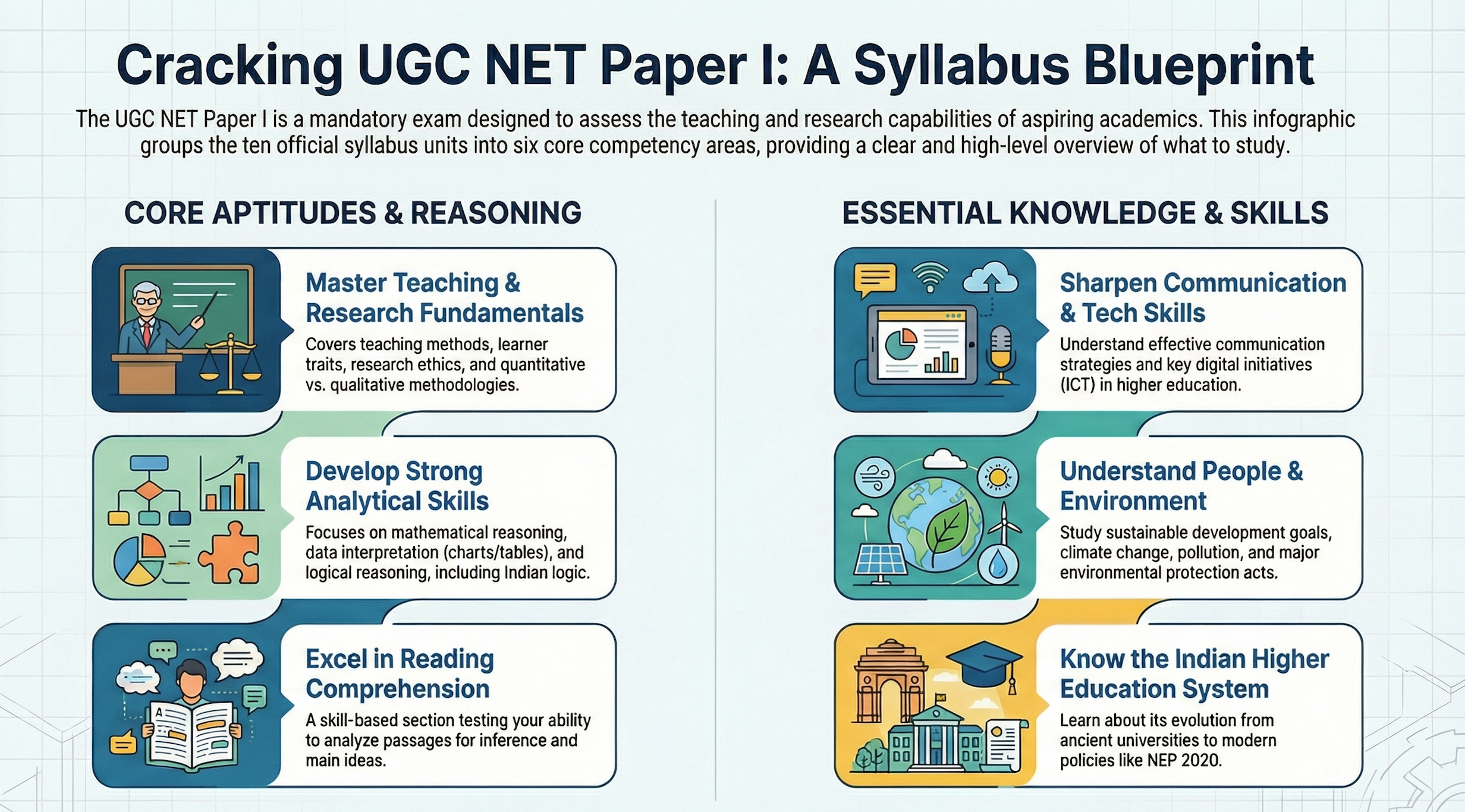
Unit 6: Logical Reasoning Syllabus for UGC NET
Logical Reasoning tests your ability to analyze arguments, identify patterns, and draw valid conclusions. This unit combines Western and Indian logic traditions.
Deductive and Inductive Reasoning in UGC NET
The syllabus covers understanding the structure of arguments including argument forms, categorical propositions, mood and figure, and both formal and informal fallacies.
You need to evaluate and distinguish between deductive and inductive reasoning approaches.
Analogies and Venn diagrams for establishing the validity of arguments are frequently tested.
Indian Logic: Pramanas and Anumana
A unique aspect of UGC NET is its inclusion of Indian logic traditions.
You must understand Pramanas including Pratyaksha (perception), Anumana (inference), Upamana (comparison), Shabda (verbal testimony), Arthapatti (implication), and Anupalabdhi (non apprehension).
The structure and kinds of Anumana, Vyapti (invariable relation), and Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference) represent advanced topics that distinguish this examination from other competitive tests.
Unit 7: Data Interpretation Syllabus for UGC NET
Data Interpretation assesses your ability to analyze and draw conclusions from various data formats commonly encountered in academic research.
Bar Charts, Pie Charts, Tables and Data Interpretation
This unit covers sources, acquisition, and classification of data along with quantitative and qualitative data distinction.
Graphical representation, including bar charts, histograms, pie charts, line charts, and table chart, forms the core content along with mapping of data.
Data interpretation questions require you to analyze presented data and answer calculation or inference based questions.
Data and governance topics explore how data informs policy decisions. Practice with diverse data formats improves both accuracy and speed in this scoring unit.
Unit 8: ICT (Information and Communication Technology) Syllabus
ICT knowledge is increasingly important for modern educators, and this unit tests your awareness of digital technologies in educational contexts.
Digital Initiatives in Higher Education and ICT Basics
The syllabus includes general ICT abbreviations and terminology along with basics of the internet, intranet, email, and audio video conferencing.
Digital initiatives in higher education, including SWAYAM, National Digital Library, and e PG Pathshala are important contemporary topics.
ICT and governance, exploring how technology enables educational administration and policy implementation, completes this unit. Staying updated with recent government digital education initiatives gives you an edge in this section.
Unit 9: People, Development and Environment Syllabus
This unit connects education with broader societal and environmental concerns that every academic professional should understand.
Climate Change, Pollution and Sustainable Development Goals
Development and environment topics cover Millennium Development Goals and Sustainable Development Goals.
Human and environment interaction, including anthropogenic activities and their impacts, is extensively covered.
Environmental issues at local, regional, and global levels, including air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, noise pollution, and various waste types, are important.
Climate change and its socio economic and political dimensions, impacts of pollutants on human health, natural and energy resources, and natural hazards and disaster mitigation strategies complete this comprehensive unit.
Knowledge of the Environmental Protection Act 1986, National Action Plan on Climate Change, Montreal Protocol, Rio Summit, Kyoto Protocol, and Paris Agreement, International Solar Alliance is essential.
Unit 10: Higher Education System in India Syllabus
This unit tests your knowledge of how higher education has evolved in India and the current governance structures that shape academic institutions.
Ancient Indian Education and Post Independence Higher Education
The syllabus covers institutions of higher learning and education in ancient India including Nalanda, Vikramashila, and Takshashila.
The evolution of higher learning and research in post independence India traces the development of universities, IITs, IIMs, and research institutions.
Oriental, conventional, and non conventional learning programs in India including distance education and open universities are important topics.
Professional, technical, and skill based education developments complete the historical perspective.
NEP 2020, UGC Policies and Governance in Higher Education
Understanding the National Education Policy 2020 and its implications for higher education is crucial for current examinations.
Value education and environmental education initiatives, along with policies, governance, and administration of higher education institutions, form contemporary content.
Knowledge of UGC regulations, NAAC accreditation, NIRF rankings, and the roles of various regulatory bodies distinguishes well prepared candidates.
UGC NET Paper 2 Syllabus 2025: Subject Wise Guide for 85 Subjects
Paper 2 is where your subject expertise shines. With 100 questions worth 200 marks, this paper demands thorough preparation in your chosen discipline.
The NTA offers 85 subjects ranging from Humanities and Social Sciences to Languages, Sciences, and Professional disciplines.
How to Choose Your Paper 2 Subject?
Your Paper 2 subject choice significantly impacts both your preparation journey and career trajectory. Selecting wisely requires understanding the alignment between your academic background and the subject syllabus.
Matching Subject with Post Graduation Discipline
The most straightforward approach is choosing the subject that matches your postgraduate degree. If you completed your Master’s in Law, select Law (Subject Code 58). This alignment ensures you already have foundational knowledge and access to relevant study materials.
However, some candidates with interdisciplinary backgrounds might find related subjects equally suitable. The key is ensuring you can cover the entire Paper 2 syllabus comprehensively within your preparation timeline.
Complete List of UGC NET Paper 2 Subjects with Syllabus PDF Links
The NTA provides official syllabus PDFs for all 85 subjects in both English and Hindi on the official UGC NET website. Let’s categorize these subjects for easier navigation.
Humanities and Social Sciences Subjects
The Humanities and Social Sciences category includes some of the most popular UGC NET subjects. Economics (Subject Code 01), Political Science (02), Philosophy (03), Psychology (04), and Sociology (05) attract thousands of candidates each cycle. History (06), Anthropology (07), Education (09), and Social Work (10) offer excellent opportunities for those with relevant academic backgrounds.
Defense and Strategic Studies (11), Home Science (12), Public Administration (14), and Population Studies (15) cater to specialized academic interests.
These subjects typically have well defined syllabus with clear unit divisions, making systematic preparation straightforward for candidates with strong conceptual foundations.
Languages and Literature Subjects
Language subjects form a significant portion of UGC NET offerings.
English (30) remains the most popular language subject with extensive competition, while Hindi (20) attracts candidates comfortable with the Devanagari script.
Regional languages, including Bengali (19), Kannada (21), Malayalam (22), Odia (23), Punjabi (24), Tamil (26), Telugu (27), Assamese (36), Gujarati (37), and Marathi (38), serve candidates across India’s linguistic diversity.
Foreign languages like Arabic (29), Chinese (32), French (39), Spanish (40), Russian (41), German (44) and Japanese (45) cater to specialized language scholars.
Classical languages, including Sanskrit (25), Urdu (28), Persian (42), and Pali (83), preserve India’s rich linguistic heritage in academic settings.
Science and Technology Subjects
The Science and Technology category includes Computer Science and Applications (87), which has become increasingly competitive given the IT sector’s growth. Environmental Sciences (89), Electronic Science (88), and Forensic Science (82) attract candidates from technical backgrounds seeking academic careers.
Geography (80) bridges physical and social sciences, covering geomorphology, climatology, and human geography. Physical Education (47) and Yoga (100) represent applied sciences with growing academic interest. These subjects typically require both theoretical knowledge and awareness of recent technological developments.
Commerce, Management and Law Subjects
Commerce (08), Management (17), and Law (58) are among the most sought after professional subjects in UGC NET.
These subjects offer direct pathways to teaching positions in business schools and law colleges. Labour Welfare/Personnel Management/HRM (55) caters to human resource specialists, while Tourism Administration and Management (93) serves the hospitality education sector.
Library and Information Science (59) serves aspiring library science educators.
Mass Communication and Journalism (63) attracts media professionals transitioning to academia.
These professional subjects typically have syllabi aligned with industry practices and contemporary developments.
UGC NET Law Syllabus 2025: Detailed Breakdown
Given LawSikho’s expertise in legal education, let’s provide an extensive breakdown of the UGC NET Law syllabus covering all ten units that law aspirants must master.
Unit 1 Jurisprudence: Schools of Law, Rights and Legal Personality
Jurisprudence forms the theoretical foundation of legal studies.
This unit covers the nature and sources of law, exploring how legal systems originate and evolve.
You must understand various schools of jurisprudence, including Natural Law, Positivism, Historical School, Sociological School, and Realist approaches.
The relationship between law and morality, concepts of rights and duties, legal personality (who can hold rights and bear duties), property, ownership, possession, and liability are essential topics.
Contemporary themes like law, poverty, and development, along with global justice and post modernist legal thought, complete this philosophical unit.
Unit 2 Constitutional and Administrative Law: Fundamental Rights, DPSP
Constitutional Law covers the Preamble, Fundamental Rights and Duties, and Directive Principles of State Policy.
You must understand the Union and State executive structures and their interrelationships, legislative powers distribution, and the judiciary’s role and powers.
Emergency provisions and special provisions for certain states are frequently tested.
Administrative Law topics include the nature and scope of administrative action, principles of natural justice, and judicial review of administrative decisions.
Knowledge of landmark constitutional cases and recent amendments is essential for scoring well.
Unit 3 Public International Law and IHL: UN, WTO and Humanitarian Law
This unit explores international legal frameworks governing relations between nations.
Topics include the definition, nature, and basis of international law, along with its sources, including treaties, customs, and general principles.
Recognition of states and governments, nationality, immigration, refugees, and internally displaced persons represent contemporary issues.
Extradition and asylum laws, the United Nations system, dispute settlement mechanisms, and the World Trade Organization’s functions are important.
International Humanitarian Law, covering the Geneva Conventions and their implementation challenges, addresses laws applicable during armed conflicts.
Unit 4 Law of Crimes: IPC, Criminal Liability and Offences
Criminal Law covers general principles of criminal liability, including actus reus (guilty act) and mens rea (guilty mind).
Stages of crime from preparation through attempt to commission, and inchoate crimes including abetment, conspiracy, and attempt are thoroughly tested.
General exceptions under the Indian Penal Code, offences against the human body, property, women, children, and the state form substantial content.
Theories and kinds of punishment, including retributive, deterrent, preventive, and reformative approaches, complete this practically important unit.
Unit 5 Law of Torts and Consumer Protection: Negligence, Strict Liability
This unit covers civil wrongs and consumer rights.
Topics include the nature and definition of tort, general principles of tortious liability, and available defenses.
Specific torts, including negligence, nuisance, trespass, and defamation, require a detailed understanding. Remoteness of damages, strict liability (Rylands v Fletcher), and absolute liability (MC Mehta case) represent landmark concepts.
The Consumer Protection Act 2019, the Motor Vehicles Act 1988 provisions on no fault liability, and the prohibitions mentioned underthe Competition Act 2002 against anti competitive practices are essential contemporary topics.
Unit 6 Commercial Law: Contract, Sale of Goods, Company Law
Commercial Law covers the essential elements under the Indian Contract Act, including offer, acceptance, consideration, and capacity.
E contracts, breach and frustration of contracts, standard form contracts, and quasi contracts are important modern additions.
Specific contracts, including bailment, pledge, indemnity, guarantee, and agency, require detailed study.
The Sale of Goods Act 1930, Partnership Act, Limited Liability Partnership Act, Negotiable Instruments Act 1881, and Company Law covering incorporation, shares, debentures, directors, and corporate social responsibility provide comprehensive commercial law coverage.
Unit 7 Family Law: Marriage, Divorce, Succession and UCC
Family Law covers personal laws across different communities. Topics include sources and schools of Hindu, Muslim, Christian, and Parsi family laws.
Marriage requirements and dissolution, matrimonial remedies, and divorce theories are extensively covered. Modern developments like live in relationships and recognition of foreign decrees represent contemporary issues. Maintenance, dower, stridhan, adoption, guardianship, succession, inheritance, wills, gifts, and wakf provide comprehensive coverage.
The ongoing debate around the Uniform Civil Code is a frequently tested contemporary topic.
Unit 8 Environment and Human Rights Law: NGT, NHRC
This unit bridges environmental protection and human rights.
Environmental topics cover the meaning and concept of environment and pollution, international environmental law, and UN conferences on environmental protection. India’s constitutional and legal framework, including the Environment Protection Act 1986, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, and the National Green Tribunal’s role, are essential.
Human rights topics cover the concept’s development, universalism versus cultural relativism, the International Bill of Rights, and group rights for women, children, persons with disabilities, and minorities.
The National Human Rights Commission and other national commissions for minorities, women, and scheduled communities complete the enforcement mechanisms.
Unit 9 IPR and IT Law: Copyright, Patent, Trademark, Cyber Crimes
Intellectual Property Rights cover concepts, theories, and international conventions, including TRIPS, Paris Convention, and Berne Convention. Copyright and neighboring rights, including subject matters, limitations, infringement, and remedies, require a detailed understanding.
Patent law covering patentability criteria, grant procedures, and protection mechanisms is frequently tested.
Trademark law, including registration, infringement, passing off, and remedies, completes the traditional IP coverage.
Geographical Indications, biodiversity, and traditional knowledge protection represent newer additions.
Information Technology Law covers digital signatures, electronic governance, electronic records, and cybercrimes, including their penalties and adjudication under the IT Act 2000.
Unit 10 Comparative Public Law: Federalism, Separation of Powers, RTI
Comparative Public Law examines different governance systems worldwide.
Topics include the purpose and challenges of comparative legal study, forms of government, comparing presidential and parliamentary systems, and federalism models in the USA, Canada, and India.
The Rule of Law in its formal and substantive versions, separation of powers across different jurisdictions, judicial independence, activism, and accountability are important comparative topics.
Constitutional review systems, amendment procedures, the Ombudsman institution, and open government principles, including Right to Information in the USA, UK, and India, provide global perspectives on governance and transparency.
How to Download UGC NET Syllabus PDF?
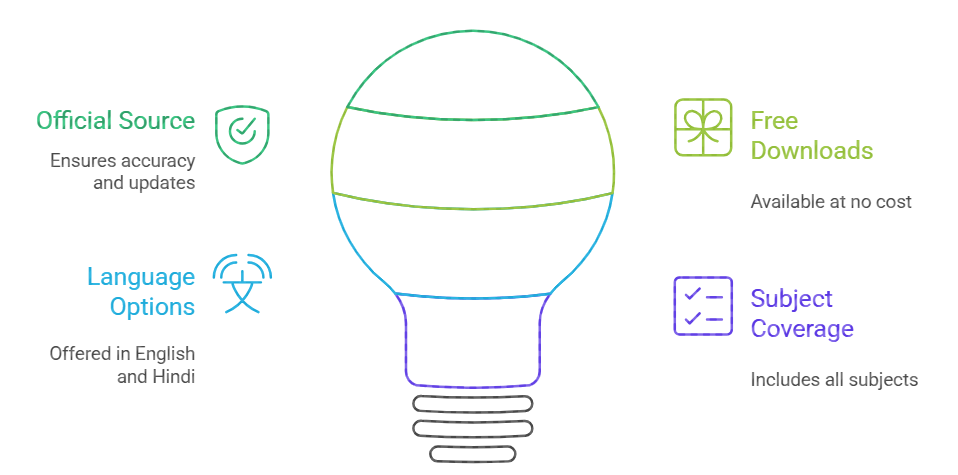
Having the official syllabus PDF ensures you’re preparing from the most accurate and updated source. The NTA UGC NET syllabus page provides free downloads in both English and Hindi for all subjects.
Official NTA Website Download Process
The NTA maintains a dedicated syllabus section on the official UGC NET website where you can access PDFs for both Paper I and all 85 Paper II subjects.
Step by Step Guide to Download Paper I Syllabus PDF
Visit the official website at ugcnetonline.in and navigate to the syllabus section. Look for “Paper I: General Paper on Teaching and Research Aptitude” link.
Click the download button for either English or Hindi version based on your preference. Save the PDF to your device for offline access during preparation.
The Paper I syllabus is approximately 3 to 4 pages covering all ten units with their detailed topics and subtopics.
Step by Step Guide to Download Paper II Subject Wise PDF
On the same syllabus page, scroll down to find the complete list of Paper II subjects organized by subject code.
Locate your chosen subject (for example, Law is Subject Code 58) and click the corresponding download link.
Both English and Hindi versions are available for most subjects.
The Paper II syllabus PDFs vary in length depending on the subject’s scope, typically ranging from 5 to 15 pages with unit wise topic breakdowns.
Syllabus Based Preparation Strategy
Understanding the syllabus is just the beginning. Converting that knowledge into a strategic preparation plan determines your success. Let’s explore how to prioritize and balance your preparation effectively.
How to Prioritize Paper I Units Based on Weightage?
Not all Paper I units carry equal importance in terms of question frequency and scoring potential. Smart preparation focuses more effort on high yield areas while ensuring basic coverage of all topics.
High Weightage Units to Focus First
Based on the previous year’s analysis, Teaching Aptitude, Research Aptitude, and Logical Reasoning consistently carry the highest weightage.
Communication and ICT are also relatively easier to master with focused preparation. Candidates who prioritize these high weightage units during early preparation phases typically perform better overall.
Time Allocation Recommendations

A balanced approach allocates approximately 15 to 20 hours each for Teaching Aptitude and Research Aptitude, given their high weightage.
Logical Reasoning and Mathematical Aptitude require 10 to 15 hours of practice focused preparation.
Data Interpretation, Comprehension, and Communication need 8 to 10 hours each.
Higher Education System and People, Development and Environment require 5 to 8 hours for content coverage.
ICT can be prepared in 5 to 6 hours if you have basic computer literacy.
Total Paper 1 preparation should span approximately 80 to 100 hours across 6 to 8 weeks for comprehensive coverage.
Depending on what you select as a subject in Paper II, the time allocation shall differ.
Balancing Paper I and Paper II Preparation
The biggest mistake candidates make is neglecting Paper 1 while focusing exclusively on their subject paper.
Remember, you must qualify separately in both papers.
A recommended approach dedicates 40% of your preparation time to Paper 1 during the initial phase, gradually shifting to 30% Paper 1 and 70% Paper 2 as the examination approaches.
During the final revision week, maintain at least 2 to 3 hours daily for Paper 1 topics to keep concepts fresh. You can also refer to this guide for more strategies and how to avoid common mistakes during preparation.
Best Books for UGC NET Based on Syllabus
Quality study materials significantly impact your preparation efficiency. Here are expert recommended books covering both papers.
Recommended Books for Paper 1
Trueman’s UGC NET/SET General Paper I by M. Gagan and Sajit Kumar remains the most comprehensive resource, covering all ten units with practice questions and previous year papers. This book’s strength lies in its balanced coverage and exam oriented approach.
For focused preparation, KVS Madaan’s NTA UGC NET Paper I from Pearson provides excellent conceptual clarity with contemporary examples.
Arihant’s UGC NET/JRF/SET Teaching and Research Aptitude offers unit wise preparation with detailed solutions.
For candidates preferring Hindi medium, Upkar’s UGC NET Paper I guide provides quality content in an accessible language.
Supplement these main books with previous year question papers from the last 5 to 10 examinations to understand question patterns and frequently tested topics.
Subject Wise Book Recommendations for Paper II
For Law (Subject Code 58), NTA UGC NET Law Paper II by Raj Rohit provides comprehensive coverage aligned with the official syllabus.
Arihant’s UGC NET Law guide offers practice questions with detailed explanations. For Constitutional Law specifically, MP Jain’s Indian Constitutional Law remains the authoritative reference. KD Gaur’s Textbook on Indian Penal Code and Avtar Singh’s Law of Contract are essential for respective units.
For other popular subjects, Commerce candidates should refer to UGC NET Commerce by CB Gupta, Political Science aspirants benefit from Shubhra Ranjan’s comprehensive guide, and English literature candidates should use Arihant’s UGC NET English Literature along with standard literary criticism texts.
Management candidates can rely on Arihant’s comprehensive guide supplemented by standard MBA textbooks for advanced topics.
Conclusion
The UGC NET examination represents a significant milestone in your academic career journey, opening doors to prestigious teaching positions and research opportunities across India’s higher education landscape.
Mastering the syllabus for both Paper I and Paper II requires systematic preparation, strategic prioritization, and consistent effort over several months. The ten units of Paper I test your foundational aptitude for teaching and research, while Paper II evaluates your expertise in your chosen discipline.
Success in UGC NET comes from understanding not just what to study, but how to study efficiently. Use this comprehensive syllabus guide as your roadmap, download the official PDFs from the NTA website, create a realistic study schedule based on the time allocation recommendations, and practice extensively with previous year papers.
Remember that thousands of candidates qualify every cycle, and with dedicated preparation, you can certainly be among them. Start your preparation today, stay consistent, and approach the examination with confidence built on thorough preparation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many subjects are available for UGC NET Paper II?
UGC NET offers 85 subjects for Paper II, including humanities, social sciences, languages, sciences, and professional disciplines. The complete list is available on the official NTA website with subject codes ranging from 01 (Economics) to 105 (Ayurveda Biology). You must select one subject while applying that preferably aligns with your postgraduate qualification.
Where can I download UGC NET Syllabus PDF?
You can download the official syllabus PDF from the NTA UGC NET website at ugcnetonline.in/syllabus-new.php. Both Paper I and Paper II syllabus are available in English and Hindi formats. Always download from official sources to ensure you have the most accurate and updated version.
What is the marking scheme for UGC NET?
Each correct answer earns 2 marks in both papers. Paper I has 50 questions worth 100 marks, while Paper II has 100 questions worth 200 marks. The total examination carries 300 marks. There is no negative marking for incorrect answers, so you should attempt every question.
Is there negative marking in UGC NET exam?
No, there is absolutely no negative marking in UGC NET examination. This candidate friendly scheme means you should attempt all 150 questions without fear of losing marks for incorrect responses. Even educated guesses are worthwhile given this marking scheme.
How many questions come from each unit in Paper I?
According to the official pattern, five questions carrying 2 marks each are typically set from each of the ten Paper I units. This means each unit contributes approximately 10 marks, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive preparation across all units rather than selective study.
Can I appear for UGC NET in Hindi medium?
Yes, UGC NET examination is conducted in both English and Hindi mediums. You can select your preferred language during application. The syllabus PDFs, question papers, and answer keys are all available in both languages to ensure equal accessibility for candidates from diverse linguistic backgrounds.
How to prepare for UGC NET Paper I based on the syllabus?
Start by downloading the official syllabus and identifying all ten units. Prioritize high weightage units like Teaching Aptitude and Research Aptitude first. Use recommended books like Trueman’s UGC NET Paper I for comprehensive coverage. Practice previous year papers to understand question patterns. Allocate approximately 80 to 100 hours across 6 to 8 weeks for thorough Paper I preparation.
What are the most important topics in UGC NET Paper I?
Teaching Aptitude topics like teaching methods, evaluation systems, and learner characteristics are highly important. Research Aptitude covering research types, ethics, and methodology is equally crucial. Logical Reasoning including Venn diagrams and Indian logic frequently appears. ICT topics on digital initiatives inHigher Education are important contemporary areas.
Is UGC NET Paper II syllabus different for each subject?
Yes, every Paper II subject has its unique syllabus designed to test domain specific expertise. The syllabus vary significantly in scope, unit structure, and topic depth. For example, Law has ten units covering various legal domains, while Computer Science covers programming, databases, networks, and artificial intelligence. Always download the specific syllabus for your chosen subject.
When was UGC NET syllabus last revised?
The UGC NET syllabus was last comprehensively revised in 2019, which became applicable from the June 2019 examination onwards. Since then, the syllabus framework has remained stable with only occasional minor updates to reflect contemporary developments in specific subjects. Major revisions typically occur every 5 to 8 years.
What is the duration of UGC NET exam?
The UGC NET examination duration is 3 hours (180 minutes) for completing both Paper I and Paper II combined. There is no break between the two papers, and candidates must manage their time effectively to attempt all 150 questions. Strategic time allocation typically involves spending about 50 to 60 minutes on Paper I and 110 to 120 minutes on Paper II.




 Allow notifications
Allow notifications